Are Lipomas Dangerous? Understanding the Risks and Causes
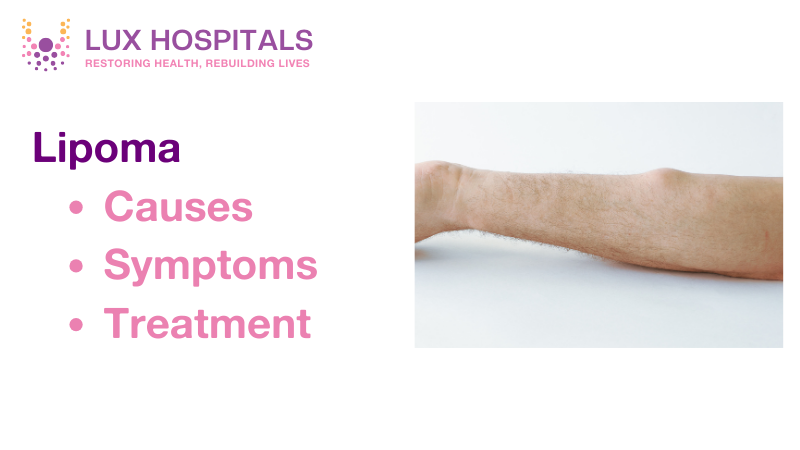
Lipomas are among the most common benign (non-cancerous) growths found under the skin. These fatty lumps are typically soft and movable, often growing slowly. Despite being harmless in most cases, people often wonder, Are lipomas dangerous? In this blog, we’ll explore the causes of lipomas, their potential risks, available treatments, and the typical costs of lipoma removal.
Let’s dive into everything you need to know about lipomas, their risks, and the options for lipoma treatment.
What is a Lipoma?
A lipoma is a soft, fatty lump that grows beneath the skin. It is made of fat cells, and its appearance is often round or oval-shaped. These growths are usually not painful but can vary in size. Lipomas can form anywhere on the body, but they are most commonly found on the upper arms, thighs, back, and neck.
While lipomas are slow-growing and generally painless, some people may experience discomfort if the lump presses on nerves or other tissues. In rare cases, lipomas may become malignant (cancerous), but this is extremely uncommon.
Causes of Lipomas
The exact cause of lipomas is not fully understood. However, several factors may contribute to their development:
- Genetics: Family history plays a major role in the development of lipomas. If a close family member has had lipomas, you may be more likely to develop them.
- Age: Lipomas are more commonly seen in adults between the ages of 40 and 60, though they can occur at any age.
- Trauma: Physical injury or trauma to the skin may contribute to the development of a lipoma, though this connection is not always clear.
- Medical Conditions: Certain conditions, such as Gardner’s syndrome and Adiposity syndrome, can lead to the growth of multiple lipomas.
Though lipomas themselves are generally harmless, they can sometimes grow large enough to cause discomfort or even interfere with daily activities.
Risks of Lipomas
Lipomas are generally not harmful. They are benign growths and do not pose a significant risk to health, as was previously stated. But in certain situations, lipomas could lead to problems:
- Size: A huge lipoma can cause pressure on surrounding muscles, nerves, or blood vessels. This can result in pain, numbness, or restricted movement.
- Location: If the lipoma is located near a joint or in a sensitive area, it may restrict mobility or cause irritation. Lipomas that develop on the scalp or face may also be more noticeable and may require removal for aesthetic reasons.
- Lipoma Rupture: While rare, a lipoma can rupture, leading to a sudden increase in size or discomfort.
- Cancerous Growth: In extremely rare cases, lipomas can turn into liposarcomas, which are cancerous tumors. These are often more firm, larger, and tend to grow rapidly. However, liposarcomas are much less common than benign lipomas.
Although lipomas are generally benign and harmless, it is crucial to keep an eye out for any changes. It’s important to see a doctor if you observe unexpected symptoms, such as pain or quick growth.
Symptoms of Lipomas
- The majority of lipomas are pliable, soft lumps that show no symptoms. But at times the following signs and symptoms may appear:
- A slow-growing, soft lump under the skin
- Pain or tenderness if the lipoma presses on nerves
- Restricted movement, especially if the lipoma is near a joint
- In rare cases, redness or warmth at the site of the lipoma
If you experience any of these symptoms, or if your lipoma grows suddenly or becomes painful, you should seek medical attention to rule out more serious conditions.
Treatment for Lipomas
While lipomas do not require treatment if they are not causing pain or discomfort, there are several options for those who wish to have them removed or treated. Here are some common treatments for lipomas:
- Surgical Removal: The most effective way to treat a lipoma is through lipoma removal surgery. This is a simple procedure in which the doctor removes the lump under local anesthesia. Surgery is often recommended if the lipoma is large, causing pain, or if it becomes bothersome.
- Liposuction: In some cases, lipoma removal can be done using liposuction. This method involves inserting a needle into the lipoma and sucking out the fatty tissue. While this method is less invasive, it may not remove the lipoma entirely, and it can sometimes regrow.
- Steroid Injections: For smaller lipomas, your doctor may recommend steroid injections to shrink the lump. This treatment does not completely eliminate the lipoma but may reduce its size.
- Laparoscopic Surgery: For deeper or larger lipomas, laparoscopic surgery may be used. This minimally invasive technique uses small incisions and a camera to remove the fatty tissue. It offers a quicker recovery time and less scarring compared to traditional surgery.
- Cryotherapy: This involves freezing the lipoma, which may cause the fat cells to die off over time. This method is not as common but can be effective for smaller lipomas.
Lipoma Removal Cost
The cost of lipoma removal can differ depending on several factors, such as the size and location of the lipoma, the type of treatment used, and your geographical location. On average, lipoma removal costs range from $500 to $3,000 per procedure.
- Surgical removal is the most common treatment and can cost anywhere from $1,000 to $3,000.
- Liposuction for lipomas tends to be less expensive, with prices starting at around $500.
- Steroid injections can cost anywhere from $100 to $500 per session.
Keep in mind that most insurance companies will cover the cost of lipoma removal if the lump is causing pain, discomfort, or interfering with daily life. However, cosmetic lipoma removals (for aesthetic reasons only) may not be covered.
When Should You Seek Treatment?
You should consider lipoma removal if the lipoma is:
- Growing rapidly
- Causing pain or discomfort
- Affecting your range of motion or daily activities
- Located in a visible or sensitive area, such as your face or neck
- Showing signs of becoming cancerous, such as firmness or a sudden change in appearance
Seeing a doctor is also crucial if you observe the formation of many lipomas or if the shape or texture of the lipoma changes. Early identification can help rule out any other potential health risks, even though most lipomas are harmless.
Conclusion
In most cases, lipomas are not dangerous and do not pose a significant health risk.They may, however, be uncomfortable, and in rare instances, lipomas may need to be removed for aesthetic or medical reasons. Any bumps on your body should be closely watched, and if you see any changes, you should speak with a healthcare professional. TTreatment options include lipoma surgery and liposuction, and the cost of removing a lipoma may vary depending on the procedure and other factors.
If you’re concerned about a lipoma, it’s always best to consult with a doctor who can assess the situation and recommend the appropriate treatment. Whether you choose lipoma treatment for medical or cosmetic reasons, the good news is that lipomas are usually benign and can be safely removed in most cases.
Frequently Asked Questions
A lipoma is a benign (non-cancerous) growth of fatty tissue that develops under the skin. It is typically soft, movable, and painless.
Lipomas are generally non-cancerous, but in rare cases, they can develop into a form of cancer known as liposarcoma. However, this is extremely uncommon.
The main risks of lipomas are related to their size and location. Large lipomas may cause pain, pressure on nearby structures, or restricted movement. They may also lead to cosmetic concerns, depending on their visibility.
Lipomas can sometimes grow back after removal, though recurrence is relatively rare. The likelihood of this depends on the completeness of the removal and the nature of the lipoma.
You should consult a doctor if you notice a new lump, if it grows rapidly, becomes painful, or if you experience any unusual symptoms associated with the lipoma.
For lipoma treatment, including diagnosis, monitoring, and surgical removal if needed, experienced general surgeons are available to manage the condition with care and precision at Lux Hospitals.