Understanding the Causes of Uterine Fibroids: What You Should Know
Uterine fibroids are harmless growths that appear inside or around the uterus. The growths are also referred to as leiomyomas or myomas. These growths are extremely common, especially in women of childbearing age. But what do uterine fibroids cause?
In this article, we will discuss the causes of uterine fibroids, their symptoms, classifications, and the treatment available so that you have a better understanding of this condition.
What Are Uterine Fibroids?
Uterine fibroids consist of fibrous and muscle tissue. They may be tiny, imperceptible nodules or large masses that alter the shape of the uterus. The growths are typically benign but may be painful and lead to other health issues.
Causes of Uterine Fibroids
Although the precise causes of uterine fibroids are still unknown, several variables are thought to be involved in their development:
1. Hormonal Imbalances
Progesterone and estrogens, menstrual-cycle regulating hormones, are found to lead to fibroid growth of the uterus. They get enlarged while a person is pregnant or experiencing a hormonal rise and during menopause when the production of these hormones is negligible.
2. Familial Susceptibility
Increasing one’s genetic chances through inherited lines predisposes them to susceptibility. A past occurrence among familial relations- in particular, grandmother, sister, and mother- points directly at them if the situation existed, leading inevitably towards uterine fibroid occurrences.
3. Ethnic and Age Factors
Fibroids are more common in women in the age range of 30 to 50, and it has been proven that African American women have a higher chance of developing them earlier in life than any other race.
4. Lifestyle Factors
Some lifestyle habits like a high red meat intake but low fruit and vegetable intake, obesity, and alcohol drinking have been proven to be risk factors for uterine fibroid development.
5. Other Medical Conditions
Illnesses such as hypertension and polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) have been linked with increased risk for uterine fibroids.
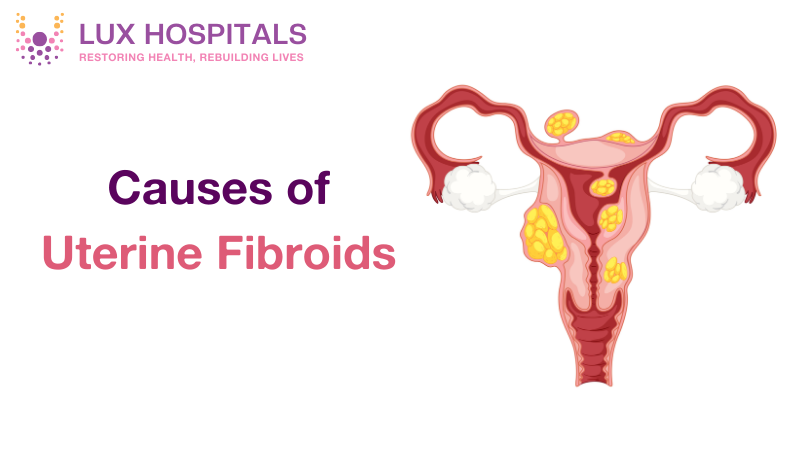
Types of Uterine Fibroids
Understanding the various types of uterine fibroids will help you grasp how they might impact your well-being:
- Intramural Fibroids: They are located within the muscular uterine wall and are the most frequent.
- Submucosal Fibroids: They are located under the lining of the uterus and may disrupt menstrual bleeding and affect fertility.
- Subserosal Fibroids: They develop on the outer layer of the uterus and usually press against organs next to it.
- Pedunculated Fibroids: They are connected to the uterine wall through a stalk and are painful when they twist.
Uterine Fibroid Symptoms
Symptoms are not always present in all women, but when they occur, they impact their quality of life. Some of the symptoms of uterine fibroids are:
- Heavy or prolonged menstrual bleeding
- Pelvic pressure or pain
- Frequent urination
- Constipation
- Painful intercourse
- Lower back pain
Uterine Fibroids Treatment Options
Treatment of uterine fibroids varies according to the size, location, and severity of symptoms. Treatment options are listed below:
- Medications: Symptoms can be treated with hormonal therapies but not with the removal of fibroids.
- Non-Invasive Procedures: MRI-guided focused ultrasound surgery can shrink fibroids without surgery.
- Minimally Invasive Surgery: Hysteroscopy or laparoscopy is employed to remove fibroids but maintains the uterus.
- Hysterectomy: Uterus removal is the recommended treatment in severe cases.
When to See a Doctor
If you notice any of the above uterine fibroid symptoms or they are starting to affect your way of life, consult a medical doctor for early diagnosis and treatment, which can prevent complications.
Conclusion
Even though the reason for uterine fibroids remains unknown, age, heredity, lifestyle, health conditions, hormonal imbalance, etc., are responsible. If you suspect you have uterine fibroids or experience symptoms, please visit a doctor to discuss with you the best course of treatment for uterine fibroids.
For the best professional treatment and the latest treatment plans, visit Lux Hospitals, where our seasoned gynaecologists give end-to-end care according to your needs.
Frequently Asked Questions
Uterine fibroids are primarily caused by hormonal imbalances (estrogen and progesterone) and genetic factors. Lifestyle and environmental influences may also contribute to their development.
Uterine fibroids can be removed through surgical procedures like myomectomy or hysterectomy. Minimally invasive options include uterine artery embolization and focused ultrasound surgery.
Yes, it’s possible to have multiple fibroids of different types at the same time, affecting other parts of the uterus.
Ultrasound, MRI, and hysteroscopy are commonly used to diagnose and determine the type and location of uterine fibroids.
Not always. Treatment depends on the size, location, symptoms, and individual health goals. Some fibroids may require monitoring, while others may need medication or surgery.
Yes, especially submucosal fibroids, which can interfere with implantation and increase the risk of miscarriage or complications during pregnancy.
Lux Hospitals offer comprehensive diagnostic and treatment options for all types of uterine fibroids. Visit Lux Hospitals for more details or to schedule an appointment.