Early Signs of Ulcerative Colitis You Shouldn’t Ignore
Ulcerative colitis (UC) is a chronic inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) that affects the colon and rectum, causing symptoms that can significantly impact a person’s quality of life. Early detection is crucial to managing the disease effectively. In this blog, we will discuss what ulcerative colitis is, its root causes, early signs and symptoms, treatment options, necessary lifestyle changes, and diet to be followed.
What is ulcerative colitis?
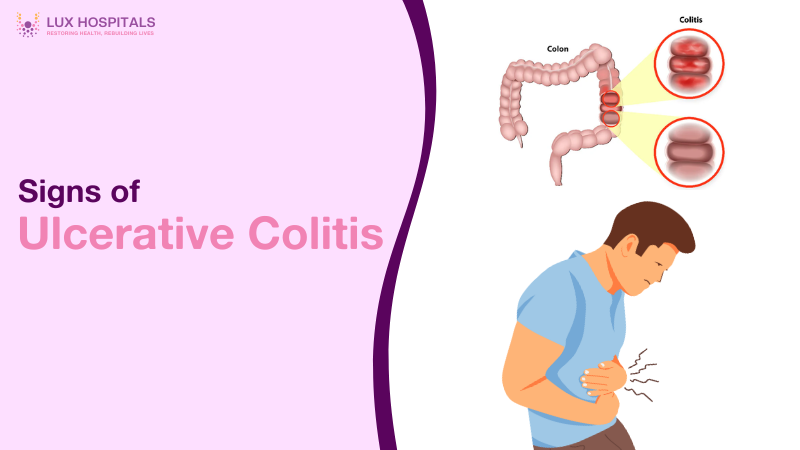
Ulcerative colitis is an autoimmune disorder that causes ulcers and inflammation in the colon and rectum. It is one of the inflammatory bowel diseases, which differ from Crohn’s disease and may occur in any part of the digestive system. UC also progresses slowly but increases in severity over time if untreated.
In ulcerative colitis, the inflammation begins in the innermost portion of the colon. It may cause chronic pain, discomfort, and complications such as malnourishment, dehydration, and the risk of developing colon cancer. Unlike irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), which only impairs bowel functioning and does not involve inflammation, UC may cause extensive damage to the lining of the intestine. The disease usually happens in cycles of flare and remission, i.e., symptoms will be poor and then improve.
Root Causes of Ulcerative Colitis
Even though the causes of ulcerative colitis are unknown, some of the reasons for the development of ulcers are as follows:
- Immune System Dysfunction: The immune system of the body becomes faulty and attacks normal cells lining the colon and thus causes inflammation.
- Genetic Factors: The genetic history of UC causes its emergence.
- Environmental Triggers: Food, stress, bacterial infection, and pollution can be a trigger for an attack.
- Gut Microbiome Dysbiosis: An excess or shortage of pathogenic and beneficial gut bacteria can result in inflammation.
Early Signs of Ulcerative Colitis
The early symptoms of UC can easily be recognized to undergo early medical treatment. Some of the typical symptoms are:
1. Frequent Diarrhea
Frequent diarrhea with mucus or blood is the starting symptom of ulcerative colitis. An increase in bowel movement is caused by inflammation of the colon.
2. Abdominal Pain and Cramping
Patients with UC usually have stabbing or constant pain in the lower abdomen. Pain increases after meals or with flare-ups.
3. Rectal Bleeding
Per rectum bleeding or hematochezia is a frightening symptom. It is caused by ulcers in the colon and rectal lining.
4. Urgency to Defecate
There is an urgent need to defecate among UC patients despite the bowels being empty.
5.Weight Loss
Unexplained weight loss is one of the symptoms of malabsorption of nutrients as a result of chronic inflammation.
6. Fatigue and Weakness
Chronic inflammation may result in excessive fatigue, and even doing daytime activities might seem like a chore.
7. Fever and Night Sweats
Night sweats accompanied by fever can be a sign of active inflammation in the body.
8. Joint Pain and Inflammation
UC can also cause symptoms beyond the digestive tract, like joint pain and inflammation, which is referred to as arthritis.
Treatment of Ulcerative Colitis
There is no cure for UC, but several treatments are employed to control the symptoms effectively.
1. Medications
Aminosalicylates (5-ASAs): Inhibit inflammation in mild and moderate colitis.
Corticosteroids: Employed for temporary relief of acute flare-ups.
Immunosuppressants: Modulate the immune system and suppress inflammation.
Biologics: Target proteins in the immune system to suppress inflammation.
2. Surgery
In extreme cases, if medications do not work, the colon must be surgically removed (colectomy).
Lifestyle Modifications for Management of Ulcerative Colitis
The addition of lifestyle changes can considerably enhance the quality of life among UC patients.
1. Stress Reduction
Stress is a documented causal factor for UC recurrences. Stress-reduction techniques such as yoga, meditation, and breathing exercises are helpful.
2. Exercise Regularly
Exercise regularly in the form of walking, swimming, or cycling to enhance intestinal health and reduce inflammation.
3. Smoking and Alcohol Abstinence
Smoking and alcohol use have been known to flare symptoms and cause exacerbations.
Dietary Advice for Ulcerative Colitis
Diet helps control UC symptoms. Although triggers are different, some dietary advice is beneficial:
1. Foods to Eat
Low-fiber foods: white rice, cooked vegetables, and lean protein reduce bowel irritation.
Probiotics: Yogurt, kefir, and fermented foods maintain the health of the gut.
Omega-3 Fatty Acids: In salmon, flaxseeds, and walnuts, these prevent inflammation.
2. Foods to avoid:
Dairy Products: Some patients with UC are lactose intolerant.
High-Fiber Foods: Raw vegetables, nuts, and whole grains can trigger symptoms.
Spicy and Fatty Foods: These irritate the digestive system.
Conclusion
Early symptoms of ulcerative colitis should be detected to have timely medical treatment. With an appropriate regimen of treatment, lifestyle alteration, and dietary modification, patients with UC can have a healthy, productive life. If you notice long-standing digestive problems, consult a doctor for a proper diagnosis and an individualized treatment regimen.
If you remain well-educated and proactive, you can be in charge of your health and reduce the role ulcerative colitis plays in your life.
Frequently Asked Questions
No, UC is not curable yet, but with proper treatment and lifestyle modification, the symptoms can be well controlled.
Not normally, but a few complications like massive bleeding, colon rupture, or colon cancer risk are life-threatening and need immediate medical care.
Yes, stress is also an important cause of symptom onset and exacerbations in UC patients.
There is genetic involvement in UC, and those with a family history of the disease are at higher risk.
The ideal diet is a low-fiber, anti-inflammatory diet with lean protein, cooked vegetables, and probiotics, which are helpful in symptom control.
Yes, daily exercise can lower stress and inflammation and enhance overall gut health.
Physicians diagnose UC using a combination of tests, such as colonoscopy, stool tests, blood tests, and imaging tests.
Crohn’s disease typically affects the entire digestive tract, but UC only affects the rectum and colon.