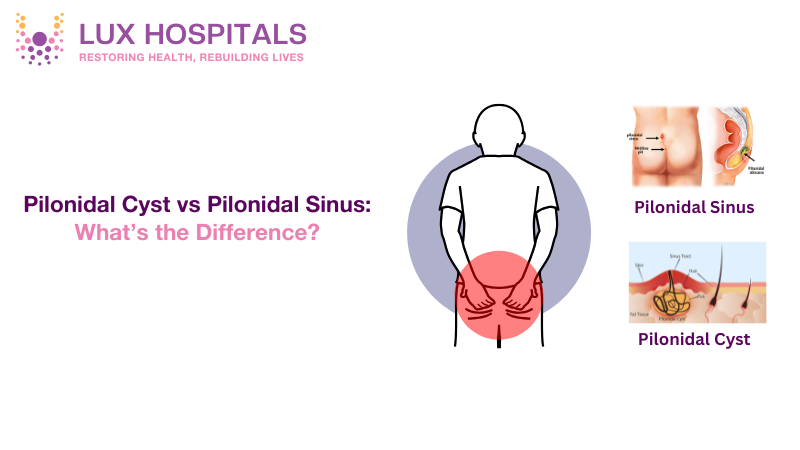
Pilonidal Cyst vs Pilonidal Sinus: Understanding the Differences
Pilonidal disease is an illness that affects the area surrounding the tailbone, inducing pain and potential complications. Is there a difference between a pilonidal cyst vs. pilonidal sinus? In order to proceed with appropriate treatment and management, it is essential that accurate differences be known. Pilonidal disease is a condition that affects the area near the tailbone, leading to discomfort and potential complications if left untreated.
Understanding the differences between a pilonidal cyst vs pilonidal sinus is crucial for effective management and treatment.
What is a pilonidal cyst?
A pilonidal cyst is a round pocket of tissue containing air or fluid usually in the buttock crease area close to the tailbone. They are normally plugged with debris, hair, and dirt, which infect them. They usually result from the occurrence of hair growing through the skin and becoming stuck, which creates inflammation and causes an abscess to develop.
What Is a Pilonidal Sinus?
A pilonidal sinus is a small tunnel or pit in the skin, which most commonly occurs in the cleft at the top of the buttocks. When the sinus gets infected, it may cause the development of a pilonidal cyst. The sinus can drain blood or pus, which is painful and smelly.
Pilonidal Cyst vs Pilonidal Sinus
It is important to understand the difference between a pilonidal cyst vs pilonidal sinus:
- Pilonidal Cyst: A sac filled with fluid that results from entrapment of hair and debris beneath the skin, resulting in infection and abscess.
- Pilonidal Sinus: A small tunnel or passageway beneath the skin that may become infected, and subsequently may result in a pilonidal cyst formation.
In short, a pilonidal cyst is a manifestation of an infected pilonidal sinus. They are connected and, if not treated, can be painfully sore.
Causes of Pilonidal Cyst and Pilonidal Sinus
The etiology of pilonidal cysts vs pilonidal sinuses is established by a few factors:
- Ingrown Hairs: Penetration of the hair into the skin may result in inflammation and formation of a cyst.
- Friction and Pressure: Chronic sitting or repeated trauma will result in irritation, thus making it more likely.
- Hormonal Changes: Hormonal variation after puberty could make people vulnerable to this process.
- Poor Hygiene: Sequestration of sweat and dirt can make the area prone to infection.
- Family History: In some instances, there may be a genetic component
Symptoms of Pilonidal Cyst and Pilonidal Sinus
The symptoms of a pilonidal cyst vs pilonidal sinus may differ based on whether the condition is chronic or acute:
Pilonidal Cyst Symptoms:
- Pain and swelling in the area next to the tailbone.
- Redness and tenderness over the skin surface overlying the affected area.
- Discharge of pus or blood, usually with a foul odor.
- Fever, in the event of severe infection
Pilonidal Sinus Symptoms:
- Small openings in the skin that drain fluid.
- Intermittent pain or discomfort, particularly when sitting.
- Recurrent infections resulting in abscess formation.
Identification of these symptoms is crucial in pilonidal cyst vs pilonidal sinus differentiation and receiving proper treatment
Treatment for Pilonidal Cyst vs Pilonidal Sinus:
Treatment varies according to the severity and nature of the condition:
Non-Surgical Treatments:
- Antibiotics: Amoxicillin and doxycycline are usually given to treat or prevent infection.
- Incision and Drainage: A simple procedure to remove pus and allow symptoms to resolve.
- Laser Hair Removal: To decrease hair in the area and prevent recurrence.
Surgical Treatments:
- Excision: This is the Removal of the cyst or sinus tract, either keeping the wound open to close or closing it with sutures.
- Flap Surgery: Reconstructive surgery to close the defect may be employed in recurrent or severe instances.
Post-operative care is essential to avoid recurrence, such as good hygiene, shaving, and avoiding sitting for long periods.
Dietary Recommendations
Healing and complication reduction can be achieved by a balanced diet:
- High-Protein Foods: Facilitate repair of tissue and immune system function.
- Fiber-Rich Foods: Encourage normal bowel action, which minimizes strain and pressure on the involved area.
- Hydration: Sufficient fluid intake contributes to overall well-being and healing of a wound.
- Vitamins and Minerals: The nutrients such as vitamin C and zinc help with skin maintenance and healing.
While diet by itself cannot heal or prevent a pilonidal cyst or pilonidal sinus, a diet rich in proteins, fibers, vitamins, and minerals can facilitate overall health and healing.
Prevention Strategies
Preventing the recurrence of pilonidal cysts vs pilonidal sinus involves the following preventive steps:
- Good Hygiene: Be clean to avoid infection.
- Hair Removal: Shave, wax, or have laser hair removal to minimize hair growth in the region.
- Avoid Long Sitting: Periodically change positions to decrease pressure on the tailbone region.
- Loose-fitting Clothes: This reduces friction and irritation on the region.
- Regular Exercise: Encourages healthy blood circulation and weight control, minimizing risk factors.
Initiating these actions will very much lessen the chance of pilonidal disease recurrence occurrence.
Conclusion
It is very important to understand the difference between a pilonidal cyst vs pilonidal sinus in order to effectively treat and prevent it. Even though they are related to each other, understanding the difference between them helps in availing proper medical attention. Good hygiene, shaving or depilation as an option, avoiding prolonged sitting, loose clothing, regular exercise, and lifestyle modifications are the preventive measures against recurrence. Seeking a medical practitioner’s advice for personalized information and treatment is important for maximum results.
Frequently Asked Questions
No. It is dependent on severity; some are treated with antibiotics and drainage, but others may need surgery.
Avoidance of pilonidal disease recurrence can be brought about by keeping oneself clean, shaving, avoiding prolonged sitting, and using loose clothing. Proper steps in prevention and treatment can be done by individuals themselves through awareness and management of etiologic causes of pilonidal cyst and sinus.
Though minor ones resolve with self-management, medical assessment is advisable to avoid complications and guarantee healing.
While it most commonly affects young adults, particularly males between puberty and age 40, it can occur at any age.
Maintaining a healthy weight, engaging in regular physical activity, and avoiding prolonged periods of sitting can help reduce the risk of developing pilonidal disease.