What is hydrocelectomy? Understanding the Procedure and Its Benefits
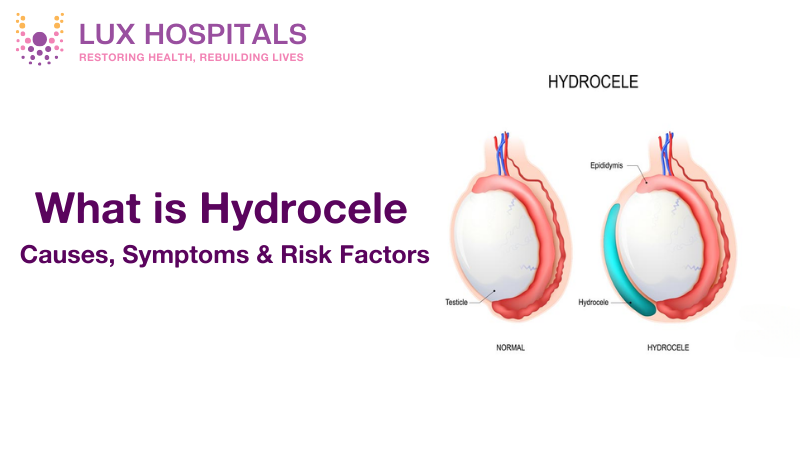
A hydrocele, a fluid-filled sac that develops around the testicle, can be surgically removed by a hydrocelectomy. Even while the condition is typically harmless, if treatment is not received, it may cause discomfort, swelling, and even problems. Hydrocelectomy provides a permanent solution for those experiencing persistent hydroceles.
In this blog, we will explore the hydrocelectomy procedure, its types, benefits, recovery process, and what to expect before and after the surgery.
Understanding Hydrocele
A hydrocele is an accumulation of fluid in the sac surrounding the testicles, known as the tunica vaginalis. It can occur in males of any age, from newborns to older adults. Hydroceles in infants often resolve on their own, while in adults, they may develop due to injury, infection, or other underlying conditions.
Causes of Hydrocele
There are several causes for the development of hydroceles, including:
- Congenital conditions: In infants, hydroceles may occur when the processus vaginalis fails to close properly.
- Infections or inflammation: Conditions like epididymitis or orchitis can lead to fluid accumulation.
- Injury or trauma: Direct injury to the scrotal area may result in hydrocele formation.
- Post-surgical complications: Some hydroceles develop after surgeries like varicocelectomy or hernia repair.
- Underlying medical conditions: Conditions such as kidney or liver disease can contribute to hydrocele formation.
Symptoms of a Hydrocele
- Swelling in the scrotum
- A feeling of heaviness
- Discomfort or pain (in some cases)
- Enlargement that may worsen over time
When is Hydrocelectomy Required?
Not all hydroceles require surgical intervention. In infants, doctors usually monitor the condition for spontaneous resolution. However, hydrocelectomy surgery is recommended in the following cases:
- The hydrocele persists beyond 12-18 months in infants.
- It causes pain, discomfort, or restricts movement.
- The hydrocele increases in size significantly.
- There is a risk of infection or hernia.
Types of Hydrocelectomy
Hydrocelectomy can be performed in a variety of ways, based on the surgeon’s inclination and the patient’s health. The following are the primary forms of hydrocelectomy:
1. Open Hydrocelectomy
This is the most common type, where an incision is made in the scrotum or lower abdomen to drain and remove the hydrocele sac. In order to stop recurrence, the surgeon could also reinforce the affected area.
2. Laparoscopic Hydrocelectomy
A laparoscopic hydrocelectomy is a minimally invasive procedure in which the hydrocele is removed using a camera-guided device after tiny incisions are created. This method is advised to promote a faster recovery and less pain following surgery.
3. Aspiration and Sclerotherapy
To prevent fluid reaccumulation in individuals who are unable to have surgery, sclerosing drugs may be injected after fluid has been drained with a needle (aspiration). But the rate of recurrence is increased with this approach.
Hydrocelectomy Procedure Steps
A hydrocelectomy procedure involves the following key steps:
1. Preoperative Preparation
- A thorough medical evaluation is conducted.
- The patient may be advised to avoid food and drink for a few hours before surgery.
- Anesthesia is administered (general or local, depending on the case).
2. Surgical Procedure
- An incision is made in the scrotum or groin area.
- The hydrocele sac is identified and carefully removed or opened to drain the fluid.
- The sac is either partially excised or everted to prevent recurrence.
- The incision is then closed with sutures.
3. Postoperative Care
- The patient is monitored in a recovery area until stable.
- Pain management medications are provided.
- Cold packs may be recommended to reduce swelling.
Benefits of Hydrocelectomy
Undergoing hydrocelectomy has several advantages, such as:
- Permanent relief from hydrocele : Eliminates the swelling and discomfort.
- Minimally invasive options are available : Faster recovery with laparoscopic hydrocelectomy.
- Improved quality of life: No restriction in movement or daily activities.
- Low risk of complications: The procedure is generally safe and has a high success rate.
Recovery After Hydrocelectomy
Recovery from hydrocelectomy surgery depends on the type of procedure performed. Here’s what patients can expect:
Immediate Post-Surgery Care
- Mild swelling and discomfort for a few days.
- Rest is recommended for at least 24-48 hours.
- Avoid lifting heavy objects or strenuous activities.
Long-Term Recovery
- Most patients recover within 2-3 weeks.
- Stitches may dissolve on their own or need removal after a week.
- Follow-up appointments are necessary to monitor healing.
Potential Risks and Complications
Although hydrocelectomy is a safe procedure, some risks include:
- Infection or bleeding
- Recurrence of hydrocele (rare)
- Scrotal swelling or bruising
- Temporary discomfort or pain
When to See a Doctor?
Seek medical attention if you experience:
- Severe pain or excessive swelling
- Persistent fever or signs of infection
- Difficulty urinating
- Any unusual discharge from the surgical site
Conclusion
A hydrocelectomy provides long-term relief from swelling and discomfort and is a dependable and successful treatment for hydroceles. Advances in surgical techniques, including laparoscopic hydrocelectomy, have reduced the invasiveness of the procedure and accelerated the healing process. Consulting with a healthcare provider can help you or a loved one decide on the best course of action for managing ongoing hydrocele symptoms.
Frequently Asked Questions
Hydrocelectomy is a surgical procedure to remove a hydrocele, a fluid-filled sac around the testicle that causes swelling.
The main cause of hydrocele is fluid accumulation around the testicle, which can result from congenital conditions, infections, inflammation, injury, or post-surgical complications.
Hydrocelectomy treatment involves surgical removal of the hydrocele. It can be done through open surgery or laparoscopic hydrocelectomy, depending on the severity. Aspiration with sclerotherapy is an alternative for non-surgical cases.
Your doctor may advise fasting before surgery, stopping certain medications, and arranging for post-surgery care.
The surgery typically takes 30-60 minutes, depending on the complexity and type of procedure used.
Possible risks include infection, bleeding, scrotal swelling, and a rare chance of recurrence.
Yes, Lux Hospitals has some of the best urologists for hydrocele treatment, offering advanced surgical options, including laparoscopic hydrocelectomy and comprehensive post-operative care.