Urinary Incontinence in Men: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatments
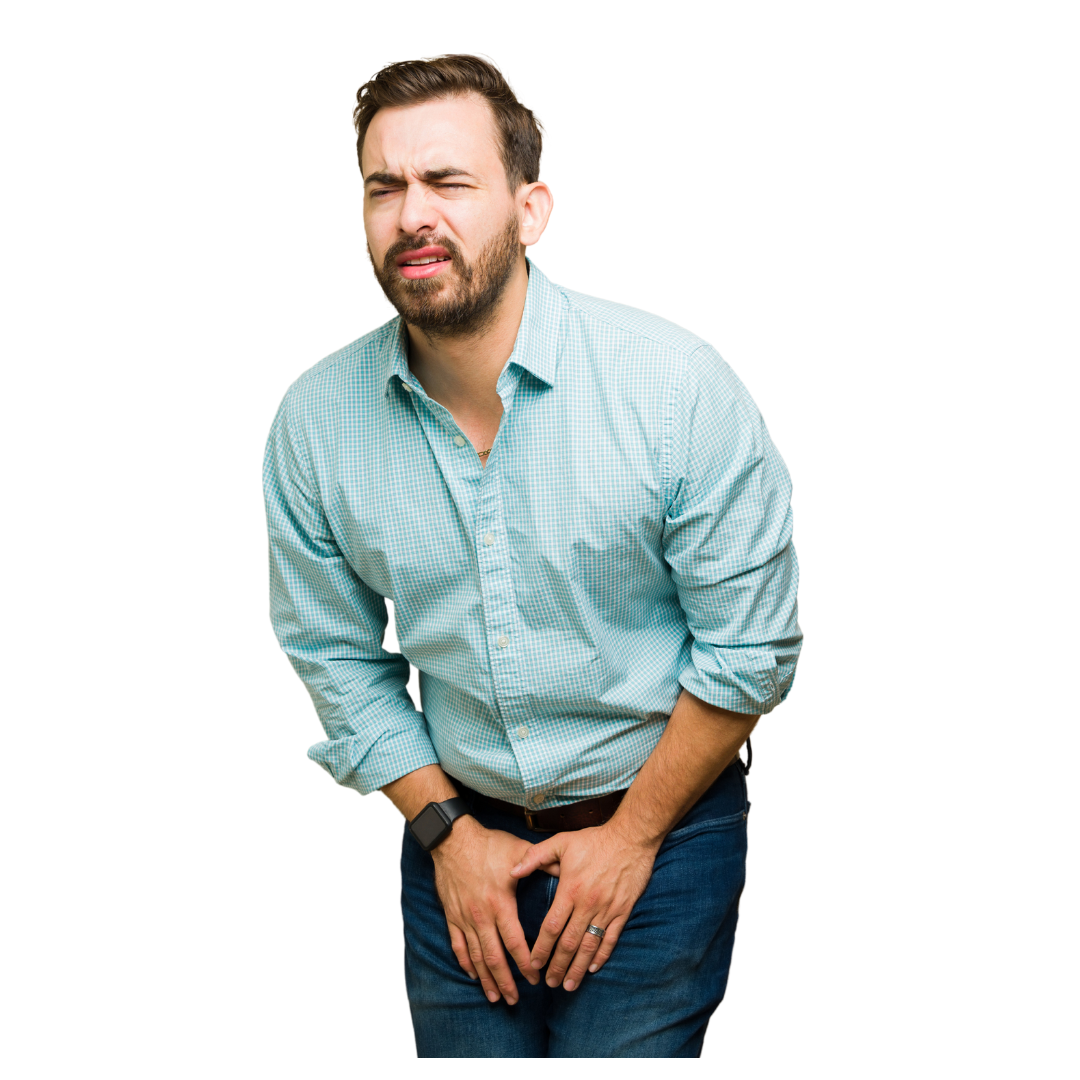

Urinary incontinence, the involuntary leakage of urine, is a condition that significantly impacts the quality of life for many men. Although it is often perceived as a women’s health issue, urinary incontinence in men is both common and treatable. Understanding the causes, recognizing the symptoms, and exploring effective treatments are essential steps in managing this condition. Statistics show that millions of men worldwide suffer from some form of urinary incontinence, making it a critical topic for awareness and action.
Understanding Urinary Incontinence in Men
Urinary incontinence is defined as the loss of bladder control, leading to the unintentional release of urine. For men, this condition can stem from a variety of factors that affect the urinary system, which includes the bladder, urethra, and associated muscles.
The urinary system in men works by storing urine in the bladder until it is ready to be expelled through the urethra. This process is controlled by the sphincter muscles, which tighten to hold urine in and relax to allow it to pass out of the body. When these muscles or nerves become weakened or damaged, urinary incontinence can occur.
While both men and women can experience urinary incontinence, the underlying causes often differ. In men, it is frequently associated with prostate issues, neurological disorders, or age-related changes, whereas in women, it is more commonly linked to childbirth and hormonal changes.
Common Causes of Urinary Incontinence in Men
Several factors can lead to urinary incontinence in men. Understanding these causes is crucial for effective diagnosis and treatment.
- Prostate Problems:
- Enlarged Prostate (Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia – BPH): As men age, the prostate gland often enlarges, pressing against the urethra and affecting bladder control. This condition, known as BPH, is one of the most common causes of urinary incontinence in men.
- Prostate Cancer and Treatments: Prostate cancer or its treatments, such as surgery and radiation, can damage the muscles and nerves that control urination, leading to incontinence.
- Neurological Disorders:
- Parkinson’s Disease, Multiple Sclerosis, and Stroke: These conditions can interfere with the signals between the brain and the bladder, leading to difficulties in controlling urination.
- Nerve Damage from Diabetes or Spinal Cord Injuries: Diabetes and spinal injuries can damage the nerves that control the bladder, causing urinary incontinence.
- Bladder Muscle Weakness:
- Age-Related Changes: As men age, the bladder muscles may weaken, making it harder to control urination.
- Overactive Bladder Syndrome: This condition causes the bladder muscles to contract involuntarily, leading to sudden and frequent urges to urinate.
- Medications:
- Diuretics, Sedatives, and Other Medications: Certain medications can increase urine production or relax the bladder muscles, leading to incontinence.
- Lifestyle Factors:
- Obesity, Smoking, Excessive Alcohol or Caffeine Intake: These factors can contribute to urinary incontinence by putting additional pressure on the bladder or irritating it.
Recognizing the Symptoms of Urinary Incontinence in men
Recognizing the symptoms of urinary incontinence is the first step toward effective management and treatment.
- Types of Urinary Incontinence:
- Stress Incontinence: Leakage occurs during physical activities such as coughing, sneezing, or lifting heavy objects. This type is often related to weakened pelvic muscles or prostate surgery.
- Urge Incontinence: A sudden, intense urge to urinate, followed by involuntary leakage. This is common in cases of overactive bladder or neurological conditions.
- Overflow Incontinence: The bladder does not empty completely, leading to frequent dribbling of urine. This can occur in men with an enlarged prostate or diabetes.
- Functional Incontinence: Physical or mental impairments, such as arthritis or dementia, prevent timely access to a bathroom, resulting in accidents.
- Warning Signs to Watch For:
- Frequency and Urgency of Urination: Needing to urinate more often than usual, especially if it disrupts daily activities or sleep.
- Accidental Leakage of Urine: Any instance of involuntary urine leakage, regardless of the amount.
- Nighttime Urination (Nocturia): Waking up multiple times during the night to urinate, which can severely affect sleep quality.

Diagnosis and When to Seek Medical Help
Early diagnosis of urinary incontinence is crucial for effective treatment and management. If you experience symptoms, it’s important to consult a healthcare provider.
- Diagnostic Tests and Procedures:
- Physical Examination and Medical History: A thorough examination and discussion of symptoms and medical history can help identify the underlying cause.
- Urinalysis and Blood Tests: These tests can detect infections, blood sugar levels, and other issues that might contribute to incontinence.
- Bladder Diary and Urodynamic Testing: Keeping a record of urination patterns and undergoing urodynamic tests can help assess bladder function.
- Imaging Tests (Ultrasound, MRI): These tests provide detailed images of the bladder, kidneys, and prostate, helping to identify structural problems.
- When to Seek Medical Advice:
- Seek medical attention if you experience frequent or severe symptoms, as early intervention can prevent complications and improve quality of life.
Treatment Options for Urinary Incontinence in Men
There are several treatment options for urinary incontinence in men, ranging from lifestyle changes to medical interventions. The best approach depends on the cause and severity of the condition.
- Lifestyle and Behavioral Changes:
- Bladder Training and Scheduled Voiding: This involves gradually increasing the time between bathroom visits to improve bladder control.
- Pelvic Floor Exercises (Kegels) for Men: Strengthening the pelvic floor muscles can help improve bladder control.
- Dietary Adjustments and Fluid Management: Reducing intake of bladder irritants like caffeine, alcohol, and spicy foods, and managing fluid intake can help control symptoms.
- Medications:
- Overview of Medications: Various medications can help manage urinary incontinence by relaxing the bladder, reducing urgency, or improving bladder muscle function.
- Potential Side Effects and Effectiveness: Discuss the potential side effects with your healthcare provider to find the most suitable medication.
- Medical Devices and Procedures:
- Urethral Inserts and Catheters: These devices can help manage incontinence by preventing leakage or aiding in bladder emptying.
- Penile Clamps and Other Supportive Devices: These devices apply pressure to the urethra to prevent urine leakage.
- Botox Injections for Overactive Bladder: Botox can be injected into the bladder muscle to reduce involuntary contractions and improve symptoms.
- Surgical Treatments:
- Sling Procedures and Artificial Urinary Sphincters: These surgeries involve placing a supportive sling or artificial sphincter to help control urination.
- Prostate Surgery and Its Impact on Incontinence: Surgery to remove the prostate or treat an enlarged prostate can impact bladder control, sometimes leading to incontinence.
- New Advancements in Surgical Treatments: Emerging surgical techniques and technologies offer new hope for men with severe incontinence.
Living with Urinary Incontinence
Living with urinary incontinence can be challenging, but there are ways to manage the condition and improve your quality of life.
- Tips for Managing Urinary Incontinence in Daily Life:
- Wear absorbent pads or protective underwear to manage leakage discreetly.
- Plan bathroom trips before leaving home and identify restroom locations when out.
- Practice good hygiene to prevent skin irritation and infections.
- Psychological and Emotional Support:
- Dealing with Stigma: Understand that urinary incontinence is a common condition and seek support from friends, family, or support groups.
- Seeking Counseling: Consider speaking with a mental health professional if urinary incontinence affects your emotional well-being.
- Importance of Patient Education and Self-Care:
- Educate yourself about urinary incontinence, its causes, and treatments to make informed decisions about your health.
- Practice self-care by following your treatment plan, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, and seeking medical advice as needed.
Conclusion
Urinary incontinence in men is a condition that can significantly impact daily life, but with the right knowledge and treatment, it can be effectively managed. Understanding the causes, recognizing the symptoms, and exploring the various treatment options are crucial steps in addressing this condition. Whether it’s making lifestyle adjustments, considering medical interventions, or exploring surgical options, there are numerous ways to regain control and improve your quality of life. If you or someone you know is experiencing urinary incontinence, don’t hesitate to seek medical advice. Early intervention can make a significant difference in managing the condition and preventing further complications.
If you’re struggling with urinary incontinence, Lux Hospitals is here to help. Our expert team offers personalized treatment plans tailored to your needs. Don’t let urinary incontinence control your life—schedule a consultation with us today and start your journey toward effective management and relief. Contact Lux Hospitals now to take the first step towards a better quality of life.