Ovarian Cyst Treatment in Hyderabad: Expert Care at Lux Hospitals
Women of reproductive age frequently develop ovarian cysts, which are fluid-filled sacs that form inside the ovaries. Some cysts can cause pain, discomfort, or issues that call for medical treatment, but the majority are benign and go away on their own. Don’t disregard signs of an ovarian cyst if you are experiencing them. At Lux Hospitals, Gachibowli, we offer advanced, personalized ovarian cyst treatment and surgery to help you feel better and protect your reproductive health.
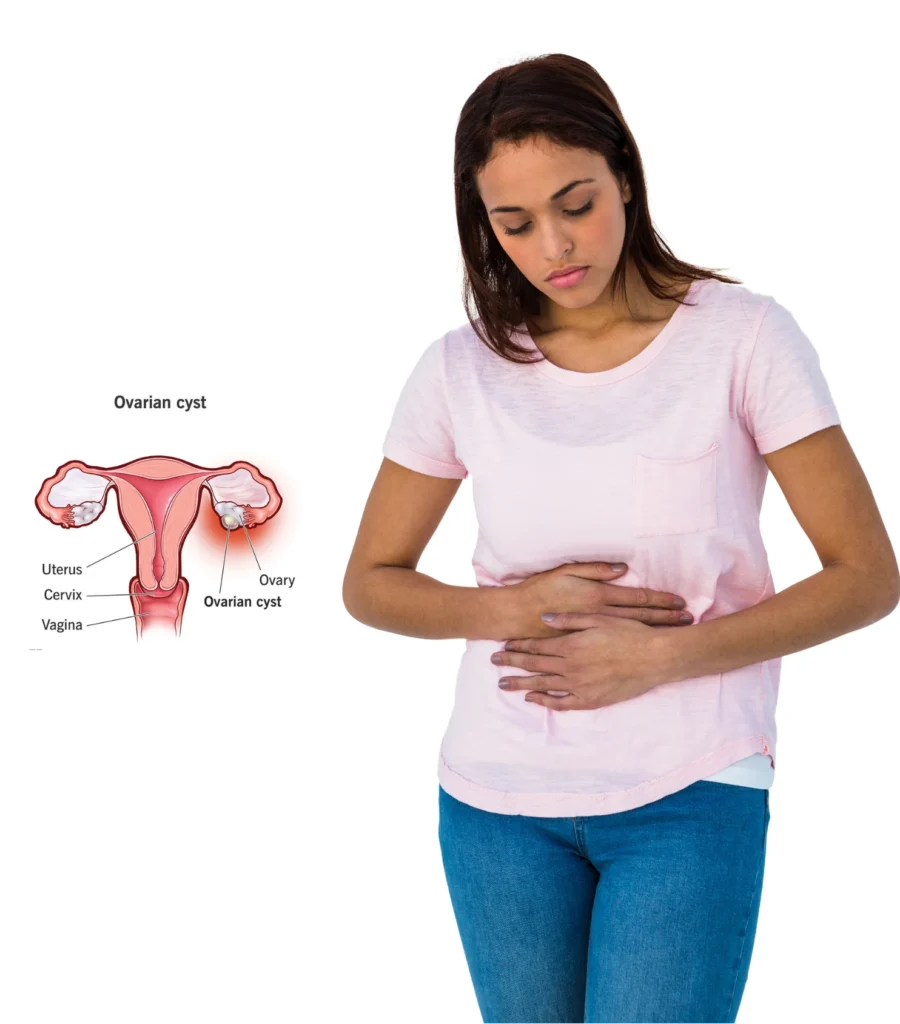
What is an Ovarian Cyst?
A sac that forms is called an ovarian cyst. It is on top of an ovary and filled with fluid or semi-solid material. Most cysts are functional and go away without treatment. However, some cysts can grow large, rupture, twist (causing ovarian torsion), or lead to other serious complications.
There are several types of ovarian cysts, including:
- Simple ovarian cysts: Usually harmless and may not require treatment.
- Hemorrhagic ovarian cysts: Filled with blood and may cause pain or internal bleeding.
- Dermoid cysts : An endometriomas Can become complex and often need removal.
- Polycystic ovaries: A hormonal condition where multiple small cysts form.
Causes of Ovarian Cysts
There are many ovarian cyst causes, including:
- Hormonal imbalances
- Endometriosis
- Pregnancy
- Pelvic infections
- Genetic factors
- Certain medications (like fertility drugs)
Understanding the causes of ovarian cysts helps tailor the proper treatment based on your health condition.
Symptoms of Ovarian Cysts
Many women with ovarian cysts may not notice any symptoms. However, larger or ruptured cysts can cause:
- Pelvic pain, especially on one side
- Bloating or a feeling of fullness in the abdomen
- Irregular periods or spotting
- Pain during intercourse or bowel movements
- Frequent urge to urinate
- Sudden, sharp pain (if a cyst ruptures or causes torsion)
If you experience these ovarian cyst symptoms, it’s essential to consult a gynecologist for evaluation and timely ovarian cyst treatment.
Ovarian Cyst Treatment Options at Lux Hospitals, Hyderabad
Treatment for ovarian cysts at Lux Hospitals is tailored to the patient’s size, kind, symptoms, and risk of consequences. To guarantee the finest results, our skilled gynecologists employ both medicinal and surgical options:
Medical Management
For small, non-problematic cysts like simple ovarian cysts, we may recommend:
- Watchful waiting with regular ultrasound monitoring
- Hormonal birth control to prevent new cysts
- Pain relievers and lifestyle advice
Surgical Intervention
If the cyst is large, persistent, causing pain, or suspected to be cancerous, ovarian cyst surgery may be necessary.
- Ovarian cyst laparoscopic surgery (Minimally invasive, quicker recovery)
- Ovarian cyst removal surgery (Cystectomy – removal of cyst only
- Oophorectomy (removal of the affected ovary, if needed)
Our team specializes in ovarian cyst laparoscopic surgery for most cases, ensuring minimal scarring, reduced pain, and faster healing.
Complications of Untreated Ovarian Cysts
Ovarian torsion (twisting of the ovary)
Cyst rupture causing internal bleeding
Chronic pelvic pain
Fertility issues
Rare risk of cancerous transformation
Side Effects of Ovarian Cyst Surgery
-
Mild pain or bloating
-
Temporary vaginal spotting
-
Infection or bleeding (rare)
-
Scar tissue formation
-
Hormonal changes (if ovary removed)
Recovery After Ovarian Cyst Surgery
Recovery varies based on the procedure:
- After laparoscopic surgery, most patients resume their jobs in a week or two.
- Recovery from open surgery could take four to six weeks.
- Abdominal pain or mild soreness is normal but controllable.
- Stay away from hard lifting and physically demanding activities for a few weeks.
To assess ovarian function and guarantee a full recovery, follow-up appointments are planned regularly.
Prevention of Ovarian Cysts
-
Regular pelvic exams
-
Managing hormonal imbalances
-
Healthy lifestyle and weight control
-
Treating conditions like endometriosis or PCOS
-
Monitoring menstrual irregularities

Dr. Harshitha Kakarla
MBBS, MS(ObGy), FMAS, DMAS, MIS Fellowship
Speciality : Gynaecologist & Laparoscopic Surgeon
Experience : 12 years

Dr. P Pragnia
MBBS, MS (ObGy), Mch (Gynaec Oncology)
Speciality : Gynaecologist & Gynaec Oncologist
Experience : 12 years
Why Choose Lux Hospitals for Ovarian Cyst Treatment in Hyderabad?
- Expert Team: Led by Dr. Pragnia, a top gynecologist and gynecologic oncologist in Hyderabad with over 16 years of experience.
- Advanced Technology: Minimally invasive and robotic-assisted ovarian cyst surgery options.
- Comprehensive Care: From diagnosis and investigation to post-op follow-ups.
- Location Advantage: Centrally located in Gachibowli, accessible across Hyderabad.
Benefits of Ovarian Cyst Surgery at Lux Hospitals
- Pain relief and improved comfort
- Lower risk of complications like rupture or torsion
- Fertility preservation (in many cases)
- Quick recovery with laparoscopic techniques
- Personalized attention and holistic support

Dr. Harshitha Kakarla
MBBS, MS(ObGy), FMAS, DMAS, MIS Fellowship
Speciality : Gynaecologist & Laparoscopic Surgeon
Experience : 12 years

Dr. P Pragnia
MBBS, MS (ObGy), Mch (Gynaec Oncology)
Speciality : Gynaecologist & Gynaec Oncologist
Experience : 12 years
LUXGPT : Your One message Away Companion

Healthcare, simplified—everything you need in one place. From sharing medical reports to getting answers about insurance or doctor consultations, just send a quick text or voice note for instant support.









