Urinary Tract Infection: Effective Management at Lux
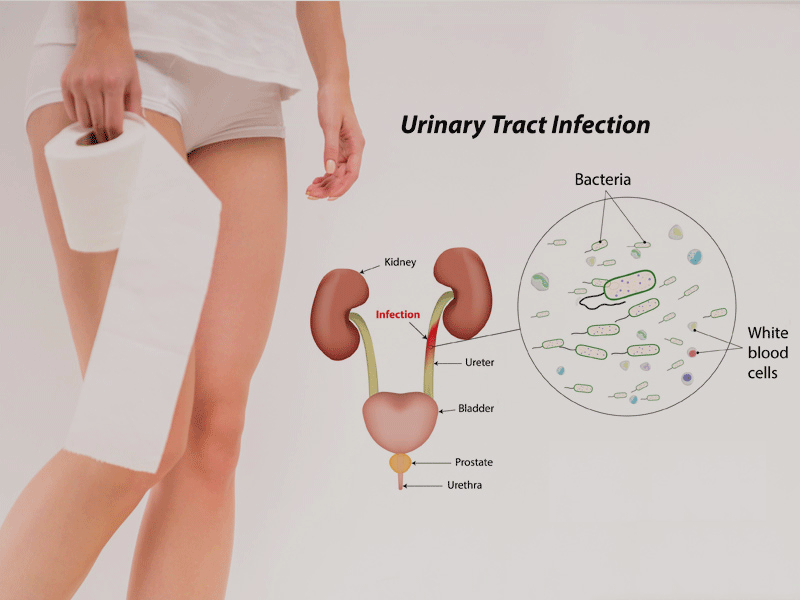
Table of Contents
Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs), often known simply as UTI disease, are infections impacting any component of the urinary system, including the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra. These are prevalent health concerns managed frequently at Lux Hospitals, where they are known to cause a variety of uncomfortable symptoms. In this discussion, we explore the signs, causes, and effective treatments for UTIs, guided by the expertise and care standards of Lux Hospitals.
What is a Urinary Tract Infection?
A Urinary Tract Infection (UTI) is an infection in any part of the urinary system, including the kidneys, bladder, ureters, and urethra. It is primarily caused by bacteria entering the urinary tract, leading to symptoms like painful urination and frequent urges to urinate. UTIs are particularly common in women but can affect anyone.
Types of Urinary Tract Infection
Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs) can be classified into several types based on the area of the urinary tract that is affected:
Cystitis (Bladder Infection): This is the most common type of UTI, where the bladder gets infected, often leading to pelvic pressure, discomfort in the lower abdomen, frequent, painful urination, and blood in the urine.
Urethritis (Urethra Infection): Infection of the urethra, the channel that carries urine from the bladder to the outside of the body. It is often characterized by a burning sensation during urination.
Pyelonephritis (Kidney Infection): A more severe form of UTI, this affects the kidneys and can cause upper back and side pain, high fever, shaking, chills, nausea, and vomiting.
Asymptomatic Bacteriuria: This occurs when bacteria are present in the urine but cause no symptoms. It’s typically harmless but can require treatment in pregnant women and individuals undergoing some types of surgery.
Treatments for Urinary Tract Infection
Treating Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs) involves several strategies to eliminate the infection and alleviate symptoms:
Antibiotics: The primary treatment for UTIs, antibiotics are prescribed based on the type of bacteria causing the infection. The duration of treatment can vary from a single dose to a week or more, depending on the severity of the infection.
Pain Relief: Over-the-counter pain relievers may be recommended to ease the pain and discomfort associated with a UTI. Medications like phenazopyridine can also help alleviate the burning sensation during urination.
Increased Fluid Intake: Drinking plenty of water helps to dilute urine and flush bacteria from the urinary tract.
Cranberry Products: Some studies suggest that cranberry juice or supplements may help prevent recurrent UTIs by preventing bacteria from adhering to the urinary tract walls.
Behavioral Changes: Adjustments such as urinating frequently, especially after sexual activity, and practicing good hygiene can help prevent future infections.
In cases of frequent or complicated UTIs, additional treatments like low-dose antibiotics over a longer period, or in severe cases, intravenous antibiotics may be necessary.
Why Choose Lux Hospitals for Urinary Tract Infection?
Lux Hospitals is renowned for its expertise in diagnosing and treating Urinary Tract Infections with a team of specialized urologists and nephrologists. We use state-of-the-art diagnostics and personalized treatment plans to ensure effective care. Our patient-centered approach and commitment to healthcare excellence make us a trusted choice for managing and resolving UTIs. Lux Hospitals also emphasizes preventive education to help patients avoid future urinary tract issues.
Diagnosis of Urinary Tract Infection
Diagnosing a Urinary Tract Infection (UTI) typically involves a few key steps to confirm the presence of an infection and identify the causative bacteria:
Urine Analysis: The most common diagnostic test for UTIs is a urinalysis, which checks for the presence of white blood cells, red blood cells, and bacteria in the urine.
Urine Culture: This test allows identification of the specific type of bacteria causing the infection and helps in choosing the most effective antibiotic for treatment.
Imaging Tests: In cases of recurrent UTIs or complicated infections, ultrasound, CT scan, or MRI might be used to rule out abnormalities or blockages in the urinary tract.
Cystoscopy: For frequent infections, a cystoscope can be inserted into the urethra to visually inspect the bladder and urethra for structural problems or abnormalities.
Causes of Urinary Tract Infection
Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs) are typically caused by bacteria that enter the urinary tract through the urethra and begin to multiply in the bladder. The primary causes include:
Bacterial Invasion: The most common culprit is Escherichia coli (E. coli), a bacteria usually found in the digestive system.
Sexual Activity: Sexual intercourse can introduce bacteria into the urinary tract, particularly in women.
Poor Hygiene: Improper wiping (from back to front) can transport bacteria to the urethra.
Urinary Retention: Incomplete emptying of the bladder can provide a breeding ground for bacteria.
Medical Conditions: Diabetes, kidney stones, and other conditions that impair the immune system or cause urine flow obstructions can increase the risk of UTIs.
Use of Certain Devices: Long-term use of catheters can also predispose individuals to urinary tract infections due to increased access for bacteria to enter the urinary tract.
Symptoms of Urinary Tract Infection
The symptoms of a Urinary Tract Infection (UTI) can vary depending on the part of the urinary system that’s infected. Common symptoms include:
- Painful Urination: A burning sensation or pain when urinating is one of the most common signs of a UTI.
- Frequent Urination: An increased urge to urinate, often with only a small amount of urine being passed.
- Urine Appearance: Cloudy, dark, bloody, or strong-smelling urine.
- Pelvic Pain: Women may experience pain in the center of the pelvis and around the area of the pubic bone.
- Other Symptoms: In more severe cases, symptoms can extend to nausea, fever, chills, and pain in the lower back or side, indicating that the infection may have reached the kidneys.
Tips to Prevent Urinary Tract Infection
Preventing Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs) involves several practical steps that can significantly reduce the risk of infection. Here are some effective prevention tips:
Stay Hydrated
Drinking plenty of fluids, especially water, helps dilute your urine and ensures that you’ll urinate more frequently, allowing bacteria to be flushed from your urinary tract before an infection can begin.
Practice Good Hygiene
For women, wiping from front to back after using the bathroom can help prevent bacteria from the anal region from spreading to the vagina and urethra. Everyone should cleanse the genital area before and after sexual activity to reduce the risk of bacterial transfer.
Urinate When Needed
Avoid holding urine for long periods. Urinating frequently can help expel bacteria from the urinary tract, thereby preventing infection.
Use Non-Irritating Feminine Products
Avoid products such as douches and powders in the genital area, which could irritate the urethra. Opt for unscented and gentle products specifically designed for sensitive skin.
Consider Cranberry Products
Cranberry juice and cranberry supplements may reduce the risk of UTIs by preventing bacteria from adhering to the urinary tract walls, though the evidence is mixed. Always check with your healthcare provider before starting any new supplement.
By integrating these preventive measures into your daily routine, you can significantly lower your risk of developing a urinary tract infection.
Conclusion
Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs) are a common but manageable health concern with the right knowledge and care. By understanding the symptoms, causes, and effective prevention strategies, you can take proactive steps to maintain urinary health. If you suspect a UTI, or for more personalized advice and treatment, visit Lux Hospitals or contact our healthcare team today. Let us help you achieve optimal urinary health!



 Chat on Whatsapp
Chat on Whatsapp