BPH Affects Urination and How to Enhance Bladder Control
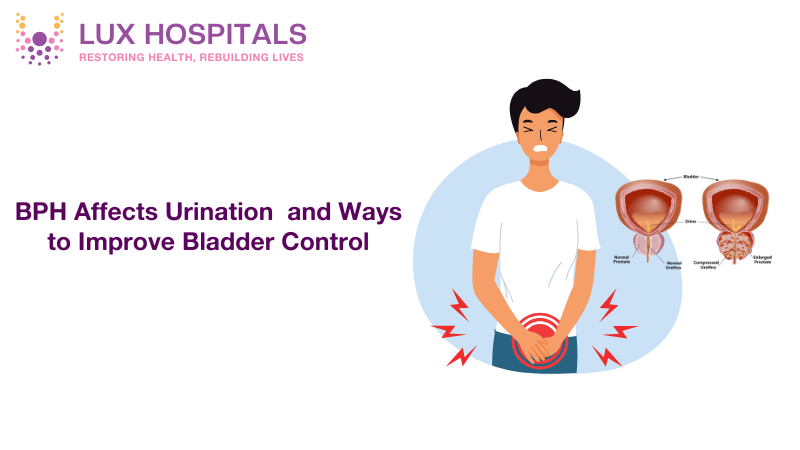
Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) is a male condition that develops with age and results in BPH Affects Urination and bladder control. BPH is not cancer, but the symptoms have a big effect on a person’s lifestyle. Men with BPH urinate frequently, have a weak stream, and do not completely empty their bladder. These symptoms disrupt sleep, work, and social life. Knowledge of the causes, symptoms, and treatment of BPH will enable individuals to cope better.
This article discusses the causes, symptoms, and treatment of BPH and offers useful advice on how to cope with bladder control. BPH Affects Urination in multiple ways, and therefore, it is important to treat symptoms early.
What is BPH?
BPH, or benign prostatic hyperplasia, is benign prostatic growth, the non cancerous swelling of the prostate gland. The prostate gland is a small gland found beneath the bladder, surrounding the urethra, the tube from which urine passes out of the body. The prostate gland will become larger with age, pushing against the urethra and causing the flow of urine to decrease. This is a benign process of aging and is linked with hormonal change.
Although BPH does not cause prostate cancer, it might cause considerable pain and interfere with regular BPH Affects Urination habits and renders daily activities troublesome.
What challenges arise when adapting to BPH symptoms?
- BPH affects daily life: It impacts almost all activities, making adaptation difficult.
- Nocturnal urination (nocturia) disrupts sleep: leading to exhaustion and reduced productivity.
- Frequent urination causes anxiety: Especially in situations where restrooms are hard to access.
- Limits social and professional activities: People may avoid long trips, social events, or work meetings.
- Difficulty emptying the bladder: This leads to frustration and discomfort, and affects overall health.
- Disrupts work and personal routines: BPH symptoms interfere with daily tasks.
- Understanding how BPH affects urination : Helps men take proactive steps for better bladder health.
When to Worry About BPH
While BPH is prevalent and generally harmless, certain symptoms require immediate medical evaluation:
- No Urination: A blockage of all urine may be an acute condition that must be evaluated immediately by a doctor.
- Blood in Urine: Hematuria may indicate bladder prolapse, infection, or other conditions.
- Severe Pain: Pain in the lower abdomen, back, or urinary tract may indicate infection or inflammation.
- Bladder Stones: Bladder stones are also a consequence of chronic BPH and create other urinary problems. BPH affects Urination severely when there are complications, and early treatment is thus essential.
Treatments for BPH
There are many treatments for managing BPH, from lifestyle modification to medical treatment.
1. Lifestyle Changes
Lifestyle modifications are often able to alleviate BPH symptoms significantly:
- Dietary Changes: Avoiding caffeine, alcohol, and spicy foods may reduce bladder irritation and urgency.
- Regular Exercise: Regular physical activity such as walking, jogging, or yoga can enhance prostate health overall as well as control symptoms.
- Hydration Balance: Adequate water consumption is needed, but limiting fluid consumption at night may lower nocturia.
- Weight Management: Having a healthy weight can lower pressure from the abdomen on the prostate and bladder. BPH Affects Urination less with lifestyle changes.
2. Medications
Physicians frequently prescribe drugs to lower BPH symptoms:
- Alpha-blockers: These medications relax muscle tissues surrounding the prostate and bladder, allowing for better flow of urine (e.g., Tamsulosin, Alfuzosin).
- 5-Alpha Reductase Inhibitors: These drugs shrink the prostate by inhibiting DHT production (e.g., Finasteride, Dutasteride).
- Combination Therapy: Certain patients like to take alpha-blockers and 5-alpha reductase inhibitors together to experience greater relief from symptoms. BPH affects urination less when the right medication is taken under medical guidance.
Conclusion
BPH is a very common but controllable disorder that may seriously impair urinary function and overall health. Symptom, cause, and therapy awareness allow men to take charge of their condition. By implementing lifestyle modifications, timely medical care, and bladder-supporting techniques, comfort during the day can be enhanced and quality of life improved.
Consult a healthcare provider if you have recurring urinary symptoms. BPH Affects Urination, but through appropriate intervention, it can be well managed. Treating BPH early will stop the worsening of symptoms and enhance general urinary function. BPH Affects Urination, but action can lead to improved long-term results.
Frequently Asked Questions
BPH Affects Urination by causing frequent urination, weak urine flow, and difficulty emptying the bladder completely.
Yes, regular exercise, a healthy diet, and hydration management can help reduce the impact of BPH Affects Urination.
If BPH Affects Urination to the extent that it causes pain, blood in urine, or inability to urinate, seek medical attention immediately.
Yes, BPH can lead to urinary incontinence, which is the loss of bladder control resulting in accidental urine leakage.
Stay hydrated, limit caffeine and alcohol, do pelvic exercises, and try medications like alpha-blockers (e.g., tamsulosin) to relax the prostate muscles.
Medications like alpha-blockers provide quick relief, but minimally invasive treatments (e.g., TURP, laser therapy) offer faster, long-term solutions.