How to Prevent and Treat Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs)
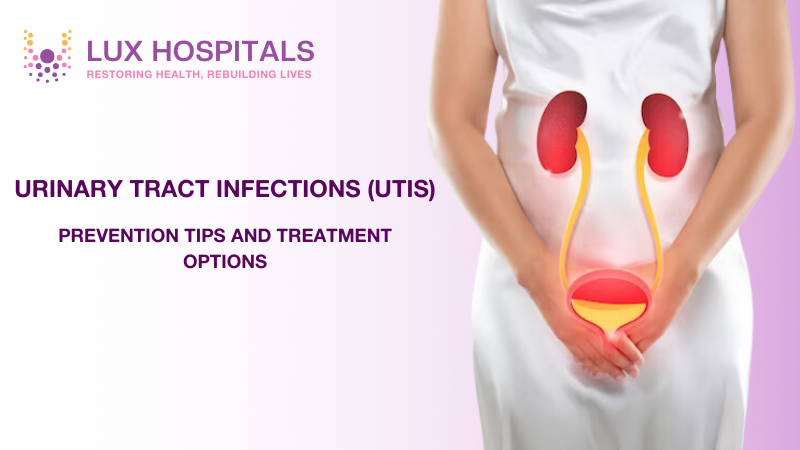
Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs) are very common medical conditions that can clearly affect daily life. While the condition is common, it can be controlled with knowledge of prevention and management, thus reducing its incidence and discomfort. The paper will focus on practical strategies to manage and prevent UTIs, ensuring optimal urinary health.
What is an Urinary Tract Infection?
A UTI is an infection caused by bacteria that have entered the urinary system, which includes the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra. Although UTIs are more common in women, men are also at risk. The key to UTI management is the effective treatment of current infections and the prevention of future infections.
Causes of Urinary Tract Infections
Knowing the causes of UTIs can help with prevention:
- Bacterial Invasion: The most common cause is Escherichia coli (E. coli), a bacterium from the bowel that can enter the urinary tract.
- Sexual Activity: Increased sexual activity can introduce bacteria to the urethra.
- Hygiene Practices: Poor hygiene, such as wiping from back to front, can transfer bacteria.
- Urinary Tract Blockages: Conditions like kidney stones or an enlarged prostate can block the flow of urine, thus making one more prone to infection.
- Weakened Immune System: If one’s immune system is weakened, they become more susceptible to infections.
Symptoms of Urinay Tract Infections
Early identification of UTI symptoms guarantees proper and early treatment:
- Burning Sensation: One classic symptom is the burning sensation when urinating.
- Frequent Urination: An increased frequency of urination.
- Cloudy or Strong-smelling Urine: The urines may become cloudy and develop a strong odour.
- Pelvic Pain: Especially in females, Pain in the pelvic region might occur.
Preventing Urinary Tract Infections
UTIs can be prevented by following healthy lifestyle practices and hygiene habits. Here are essential ways:
1. Practice Good Hygiene
Wipe Properly: Wipe from front to back to prevent the spread of bacteria to the urethra.
Clean Before and After Sex: Washing the genital area before and after sex helps reduce the transfer of bacteria.
2. Drink Enough Fluids
Drink Plenty of Water: Staying hydrated helps dilute urine and flush bacteria from the urinary tract.
3. Urinate Often
Do not hold the Urine: Frequent urination washes the bacteria out of the urinary tract, thereby decreasing the chance of infection.
4. Use Probiotics
Add Probiotics: Probiotics are good bacteria that maintain a good balance of bacteria, thus preventing UTIs
5. Avoid Irritants
Be Smart about Products: Stop using feminine hygiene products, such as douches and powders, that irritate the urinary tract
6. Consider Alternative Birth Control Methods
Opt for non-spermicidal alternatives: Spermicides and diaphragms may increase the risk of UTIs. Consider alternative contraceptives.
Managing UTIs
In fact, properly managing a UTI is crucial for the avoidance of complications and reducing the chances of getting recurrent infections. Common management approaches are hereby illustrated:
1. Antibiotics
Take Prescribed Antibiotics: The doctor is likely to prescribe some antibiotics that deal directly with bacteria causing a urinary infection. It would help if the course was completed even though symptoms improve or recede.
2. Pain Relief
Alleviate Discomfort: Acetaminophen or ibuprofen are examples of over-the-counter pain medications that can help lessen the pain and suffering related to UTIs.
3. Increase Fluid Intake
Flush Out Bacteria: Drinking water may help clear bacteria from the urinary system, which can promote recovery.
Preventing Recurrent UTIs
Women who experience recurrent UTIs may need more active measures to prevent recurrence:
1. Continuous Low-Dose Antibiotics
Prophylactic Treatment: A doctor may sometimes prescribe a long-term course of low-dose antibiotics to prevent repeated infections.
2. Postcoital Antibiotics
Targeted Prophylaxis: When UTIs are associated with sexual activity, a single post-intercourse dose of antibiotics can be effective.
3. Natural Remedies
Cranberry Products: Some evidence indicates that cranberry juice or supplements may prevent bacteria from adhering to the urinary tract’s walls, but more studies need to be carried out to establish their effectiveness.
Conclusion
UTIs can be controlled and mostly prevented with the right approach. One will be able to reduce their chances and usually enjoy better urinary health by creating awareness of causes and symptoms, leading healthy habits, and seeking early medical attention. Recurring UTIs are better addressed by talking with a healthcare provider in the development of a prevention and management plan.Properly treating the urinary tract and giving full attention to continuous care can avoid infections and, on that note, result in a greater quality of life. Stay hydrated, practice good hygiene, and take charge of your health to keep UTIs at bay.