Understanding Menorrhagia: What Causes Heavy Menstrual Bleeding?
Experiencing heavy menstrual bleeding can be distressing and disruptive to daily life. Suppose you find yourself changing pads or tampons too frequently or noticing large period blood clots. In that case, you may be dealing with menorrhagia a condition characterized by excessive or prolonged menstrual bleeding. While some women naturally have a heavier flow, persistent and abnormally heavy bleeding may indicate an underlying health issue.
In this article, we’ll explore the possible causes of heavy menstrual bleeding, the symptoms, and the available treatment options to help you manage this condition better.
What Is Menorrhagia?
Menorrhagia is defined as heavy menstrual bleeding that lasts more than seven days or needs frequent sanitary product changes because of significant blood loss. It can lead to fatigue, anemia, and difficulty carrying out daily activities. Although some menstrual variability is normal, extremely heavy periods should not be ignored.
Symptoms of Heavy Menstrual Bleeding
- Soaking through pads or tampons within one to two hours
- Passing large blood clots during periods, often bigger than a quarter
- Prolonged bleeding lasting more than a week
- Anemia symptoms, such as fatigue, dizziness, or shortness of breath
- Needing to use double sanitary protection (tampons and pads together)
It’s crucial to speak with a healthcare professional to determine possible causes if you frequently have these symptoms.
Common Causes for Menorrhagia
There are numerous causes of heavy menstrual bleeding. Establishing the cause will assist in deciding the optimal treatment.
1. Hormonal Imbalances
Hormones plays a crucial role in controlling your menstrual cycle. There is an imbalance of estrogen and progesterone, which causes the uterine lining to grow too much, leading to heavy bleeding. PCOS and thyroid disease can also interfere with hormones.
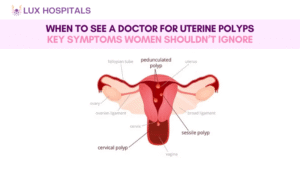
2. Uterine Fibroids and Polyps
Noncancerous tumors such as fibroids and polyps in the uterus may lead to period clots and heavy menstrual bleeding. Fibroids are tumors of the muscle, and polyps are small benign growths on the lining of the uterus. Both may lead to irregular and prolonged menstruation.
3. Adenomyosis
Adenomyosis is a condition where the uterine lining invades the muscle wall of the uterus, leading to poor cramping, heavy bleeding during menstruation, and clots. Adenomyosis is found in women over the age of 30 and those who have had more than one child.
4. Bleeding Disorders
Certain women have inherited bleeding disorders, including von Willebrand disease, which interfere with the clotting ability of the blood. This results in heavy menstrual bleeding and heavy menstrual blood loss.
5. Use of Certain Medications
Hormonal contraceptives, anticoagulants, and anti-inflammatory agents all may produce abnormal menstrual bleeding. While birth control pills will make menstruation regular, some women will have heavier periods or breakthrough bleeding because of their use.
6. Endometriosis
Endometriosis is an agonizing illness where uterine tissue occurs outside the uterus, leading to inflammation, cramping, and heavy menstrual periods. Endometriosis victims typically experience menstrual cramps and heavy clots during menstruation.
7. Pregnancy Issues
Early pregnancy complications, including miscarriage and ectopic pregnancy, can lead to heavy bleeding and menstrual clots. If pregnancy issues are suspected, seek urgent medical attention.
8. Cancer
Although uncommon, cancers of the cervix, uterus, or ovaries can lead to abnormal uterine bleeding. If you have abnormal bleeding, postmenopausal bleeding, or severe pelvic discomfort, see your physician.
Diagnosis and Treatment for Heavy Menstrual Bleeding
Diagnosing Menorrhagia
To find the reason behind heavy monthly bleeding, a physician may do a number of tests:
- Pelvic exam to check for abnormalities
- Ultrasound to detect fibroids or polyps
- Blood tests to assess hormone levels and anemia
- Endometrial biopsy to examine uterine lining tissue
- Hysteroscopy to look inside the uterus with a small camera
Treatment Options
Several therapy approaches can help control heavy menstrual bleeding, depending on the underlying cause:
1. Medications
- Hormonal contraceptives to control periods: pills, IUDs, or injections
- NSAIDs (nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medicines) help lessen pain and blood flow
- Desmopressin or tranexamic acid to aid in blood coagulation
- Iron supplementation to prevent excessive blood loss-related anemia
2. Medical Procedures
- Endometrial ablation: A procedure to remove or thin the uterine lining
- Myomectomy: Surgery to remove fibroids while preserving the uterus
- Hysterectomy: In severe cases, removing the uterus may be necessary
Managing Heavy Menstrual Bleeding Naturally
If you are more inclined towards natural remedies, try lifestyle modifications that will help reduce heavy menstrual bleeding:
1. Well-Balanced Diet
- Consume iron foods such as spinach, lentils, and red meat to avoid anemia
- Consume vitamin C food to enhance iron absorption
- Take plenty of water and cut down on caffeine and alcohol intake
2. Regular Physical Exercise
Exercise regularly to balance hormones and ease menstrual cramps. Do not exercise too much, though, as it can upset your cycle.
3. Use Herbal Remedies
Certain women have reported getting relief with herbal supplements such as ginger, turmeric, and raspberry leaf tea, which could be used to ease inflammation and balance menstrual flow.
4. Manage Stress
Excessive stress can influence the balance of hormones and lead to heavy bleeding during menstruation. Use yoga, meditation, or deep breathing to control Stress well.
When to Consult a Doctor
While heavy menstruation every now and then is never necessarily anything to worry about, consult a doctor if you find:
- Heavy or prolonged bleeding for longer than 7 days
- Recurrent passing of big blood clots
- Severe fatigue, dizziness, or indicators of anemia
- Irregular menstrual cycles or intermenstrual bleeding
Conclusion
However managing heavy menstrual bleeding can be challenging, your general health can be improved by identifying the cause and getting the right treatment. Regardless of whether the reason is a disease, fibroids, or a hormone imbalance, menorrhagia requires proactive therapy.
Don’t put off seeing a doctor if you experience severe or prolonged heavy menstrual bleeding. You can manage your menstrual health and enhance your long-term health with the proper care.
How to stop heavy menstrual bleeding with clots?
Managing heavy bleeding may require a combination of treatments such as hormonal therapy, iron supplements, NSAIDs, or medical procedures like endometrial ablation. Consult a doctor for personalized treatment.
What causes severe menstrual cramps and heavy bleeding?
Conditions like endometriosis, fibroids, adenomyosis, or hormonal imbalances can lead to severe cramps and heavy bleeding. A medical evaluation can help identify the underlying cause.
What food causes heavy menstrual bleeding?
Foods high in phytoestrogens like soy products, excess caffeine, alcohol, and processed foods may contribute to hormonal imbalance, potentially leading to heavier periods.
Can heavy menstrual bleeding cause anemia?
Yes, excessive blood loss can lead to iron deficiency anemia, causing fatigue, dizziness, and weakness. Iron-rich foods or supplements can help manage anemia.
Can heavy menstrual bleeding cause weight loss?
Significant blood loss can sometimes contribute to unintentional weight loss, especially if accompanied by underlying conditions like thyroid disorders or endometriosis. Seek medical advice if you experience unexplained weight changes.