Hematuria Symptoms: Powerful Signs You Shouldn’t Ignore
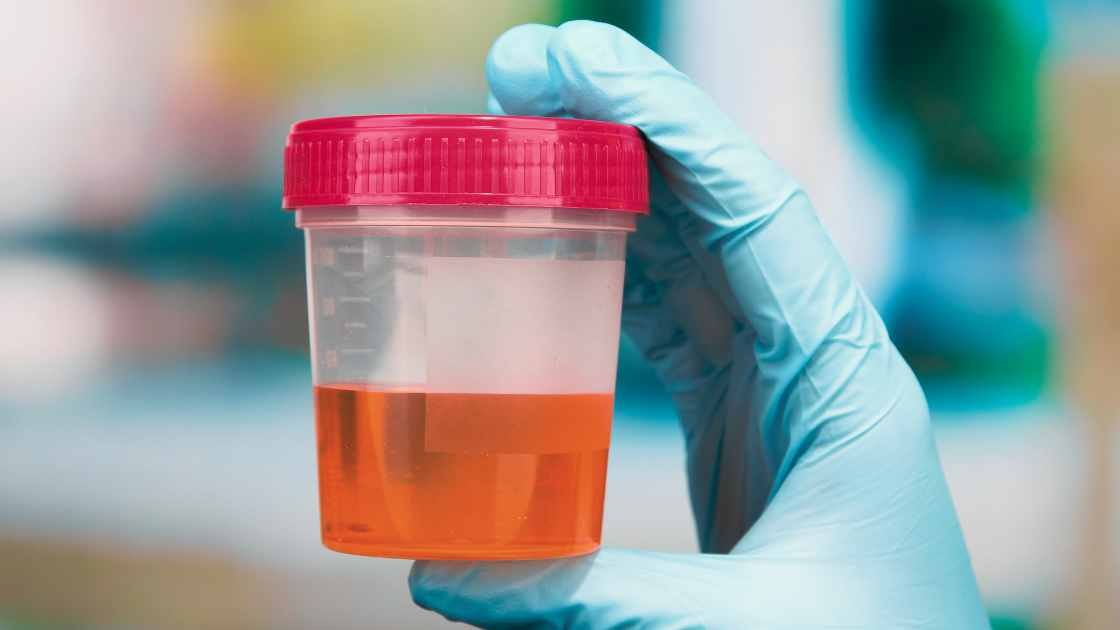

Hematuria, or the presence of blood in the urine, can be a concerning hematuria symptom that may indicate various underlying health issues. Understanding hematuria symptoms is crucial for early diagnosis and effective treatment. This comprehensive guide will delve into the symptoms of hematuria, exploring what they mean, their potential causes, and when you should seek medical attention.
What Is Hematuria?
Hematuria is a medical condition where blood is found in the urine, which can be either visible to the naked eye (gross hematuria) or detected only through laboratory tests (microscopic hematuria). While it might be alarming, hematuria is not a disease in itself but a symptom of an underlying issue. Recognizing hematuria symptoms can be crucial for diagnosing conditions ranging from urinary tract infections to more severe health concerns.

Common Hematuria Symptoms
Understanding the Common Hematuria Symptoms:
Visible Blood in Urine (Gross Hematuria)
One of the most obvious hematuria symptoms is seeing blood in the urine. This can range from a slight pink or red tint to the urine to a darker, more alarming color. The blood may appear sporadically or be consistently present. If you notice this change, it’s essential to seek medical evaluation to determine the cause.
Dark or Tea-Colored Urine
Sometimes, the blood in the urine might not be bright red but rather a dark or tea-colored hue. This change in color can be a subtle indication of hematuria and might not always be immediately noticeable. Regular monitoring of urine color can help in identifying this symptom.
Pain or Discomfort
Hematuria can sometimes be accompanied by pain or discomfort in the lower abdomen or pelvic area. This pain can vary from mild to severe and may be either intermittent or continuous. It is often associated with conditions like kidney stones or urinary tract infections.
Frequent Urination or Urgency
In some cases, hematuria might be accompanied by increased frequency of urination or a sense of urgency. This is often seen in cases where a urinary tract infection or bladder inflammation is present alongside hematuria symptoms.
Painful Urination (Dysuria)
Painful urination, or dysuria, can occur along with hematuria and is characterized by a burning or stinging sensation while urinating. This symptom is commonly associated with urinary tract infections (UTIs) and should be addressed promptly.
Abdominal or Flank Pain
Persistent pain in the lower abdomen or flanks can sometimes be a symptom of hematuria. This pain can be either dull or sharp and may vary in severity. It is often linked to conditions such as kidney stones or bladder infections.
Unexplained Weight Loss or Fever
Although less common, unexplained weight loss or fever alongside hematuria could indicate a more serious underlying condition such as a tumor or chronic infection. These symptoms necessitate a comprehensive assessment by a healthcare professional.
Potential Causes of Hematuria
Understanding the potential causes of hematuria is crucial for accurate diagnosis and treatment. Some common causes include:
Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs)
UTIs are a prevalent cause of hematuria and are often accompanied by symptoms such as painful urination, frequent urination, and lower abdominal discomfort. Bacteria in the urinary tract can cause inflammation and bleeding.
Kidney Stones
Kidney stones are hard deposits that form in the kidneys and can cause significant pain and hematuria as they pass through the urinary tract. Symptoms often include severe flank pain, nausea, and blood in the urine.
Bladder or Kidney Infections
Infections in the bladder or kidneys can cause hematuria along with symptoms such as pain, fever, and frequent urination. These infections need immediate treatment to avoid potential complications.
Trauma or Injury
Physical trauma or injury to the urinary tract or kidneys can result in hematuria. This can be due to accidents, sports injuries, or medical procedures.
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH)
In men, an enlarged prostate (BPH) can sometimes cause hematuria, particularly in older adults. BPH may also lead to urinary frequency, urgency, and difficulty in urination.
Bladder or Kidney Cancer
Hematuria can occasionally be a sign of more severe conditions like bladder or kidney cancer. This is especially concerning if the blood is persistent and accompanied by other symptoms such as unexplained weight loss or persistent pain.
Medications
Certain medications, such as anticoagulants or blood thinners, can cause bleeding in the urine. If you are on such medications, it’s essential to discuss any unusual symptoms with your healthcare provider.
When to Seek Medical Attention
If you experience hematuria symptoms, it’s crucial to seek medical attention to determine the underlying cause. Immediate evaluation is necessary if:
1.You Notice Blood in Your Urine: Whether it’s visible or detected through tests, any presence of blood in the urine should be evaluated by a healthcare professional.
2.Accompanied by Severe Pain: If hematuria is accompanied by severe pain or discomfort, it may indicate a more serious condition requiring prompt attention.
3.Persistent Symptoms: If the symptoms persist over time or worsen, it is essential to seek medical help to prevent complications and receive appropriate treatment.
4.Additional Symptoms: The presence of additional symptoms such as fever, weight loss, or unexplained fatigue should be evaluated thoroughly.
Diagnostic Tests for Hematuria
To diagnose the cause of hematuria, healthcare providers may recommend several tests, including:
Urinalysis
A urinalysis is a common test used to detect the presence of blood and other abnormalities in the urine. It helps in identifying infections, kidney stones, or other issues.
Urine Culture
If a urinary tract infection is suspected, a urine culture may be performed to identify the bacteria and determine the most effective antibiotic treatment.
Imaging Studies
Imaging tests such as ultrasound, CT scans, or MRIs can provide detailed images of the urinary tract and kidneys to identify any structural abnormalities or tumors.
Cystoscopy
A cystoscopy involves inserting a thin tube with a camera into the bladder to visually inspect the bladder lining and urethra. This procedure can help diagnose bladder issues or tumors.
Treatment Options for Hematuria
Treatment for hematuria depends on the underlying cause. Some potential treatment options include:
- Antibiotics for UTIs
If a urinary tract infection is the cause of hematuria, antibiotics will be prescribed to clear the infection and alleviate symptoms. - Pain Management
For conditions like kidney stones, pain management may be necessary to alleviate discomfort while the stones pass or are treated. - Surgery
In cases of significant kidney stones or tumors, surgical intervention may be required to remove or address the underlying issue. - Lifestyle Changes
For conditions like benign prostatic hyperplasia, lifestyle changes and medications may help manage symptoms and prevent further complications. - Follow-Up Care
Regular follow-up with a healthcare provider is essential to monitor the condition, ensure effective treatment, and prevent recurrence.
Conclusion
Hematuria symptoms, while sometimes alarming, can often be managed effectively with prompt medical attention and appropriate treatment. Understanding these symptoms and seeking timely evaluation is crucial for diagnosing and addressing any underlying health issues. If you experience any signs of hematuria, don’t hesitate to consult a healthcare provider to ensure your health and well-being.
Frequently Asked Questions
Common causes include urinary tract infections (UTIs), kidney stones, bladder or kidney infections, trauma, benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), certain medications, and, in rare cases, bladder or kidney cancer.
Yes, certain medications such as blood thinners or anticoagulants can cause hematuria. Inform your doctor if you notice blood in urine while taking these medications.
Diagnosis may involve urinalysis, urine culture, imaging studies (ultrasound, CT, MRI), and cystoscopy to determine the underlying cause.
Treatment depends on the cause and may include antibiotics for UTIs, pain management for kidney stones, surgical interventions for tumors or large stones, and lifestyle changes or medications for BPH.
Prevention involves maintaining good urinary tract health: staying hydrated, practicing proper hygiene, managing chronic conditions, and regular check-ups if you have risk factors.