Ulcerative Colitis Treatment in Hyderabad: Expert Care at Lux Hospitals Introduction
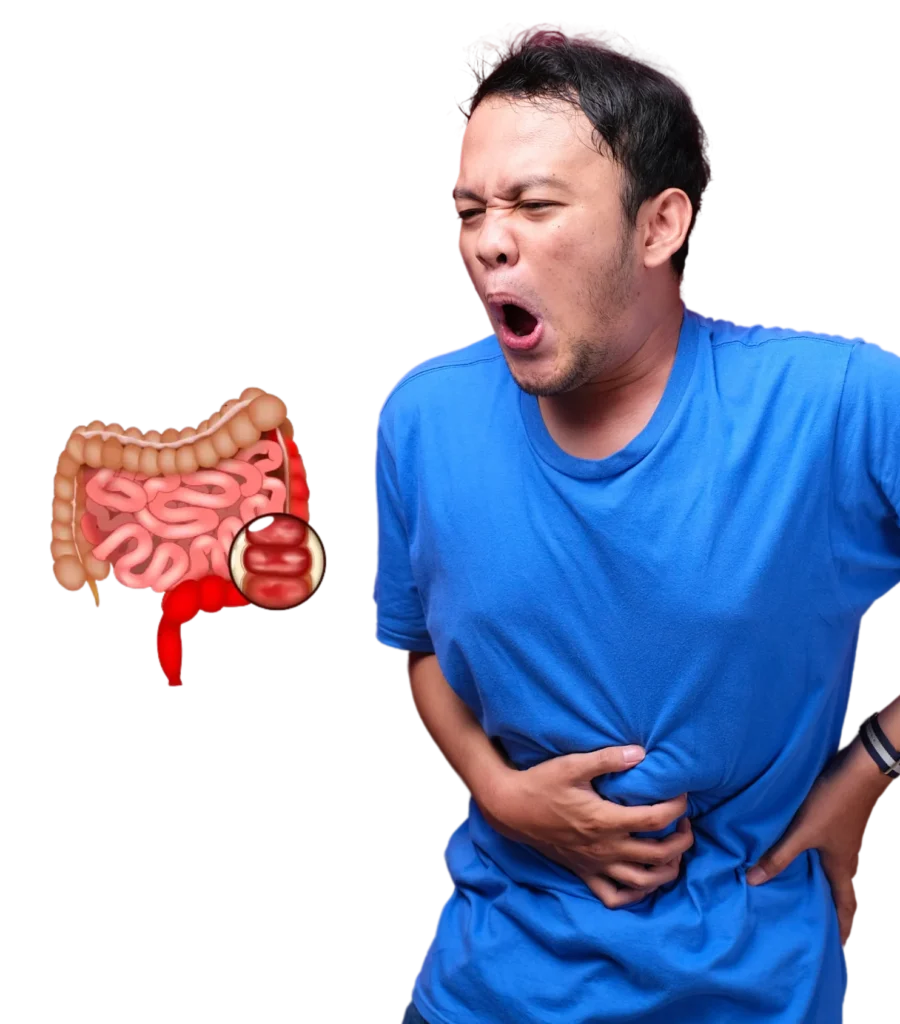
A chronic inflammatory disease of the large intestine, ulcerative colitis causes symptoms like diarrhea, rectal bleeding, and abdominal pain. Good ulcerative colitis therapy in Hyderabad is crucial for symptom management and life quality enhancement. Lux Hospitals’ cutting-edge, customized care ensures the best outcomes for our patients. Our knowledgeable gastroenterologists provide innovative treatment for mild and severe ulcerative colitis, focusing on long-term comfort and patient well-being.
What is Ulcerative Colitis?
Ulcerative colitis is a type of inflammatory bowel disease treatment that causes inflammation and ulcers in the lining of the colon and rectum. While the exact cause remains unknown, it is believed to be triggered by an overactive immune response. If left untreated, ulcerative colitis can lead to severe complications requiring immediate medical attention.
Causes of Ulcerative Colitis
The symptoms of ulcerative colitis symptoms range from mild to severe, depending on the extent of inflammation. Common symptoms include:
- Persistent diarrhea with blood or pus
- Abdominal pain and cramping
- Urgency to pass stools
- Weight loss and fatigue
- Fever in severe cases
- Loss of appetite
- Anemia due to chronic blood loss
Recognizing these symptoms early and seeking the best treatment for ulcerative colitis can help prevent complications and improve overall health.
Symptoms of Ulcerative Colitis
- Immune System Dysfunction: The immune system mistakenly attacks healthy cells in the digestive tract, leading to inflammation.
- Genetic Factors: A family history of ulcerative colitis increases the risk.
- Environmental Triggers: Certain infections, stress, and diet may trigger flare-ups.
Treatment Options for Ulcerative Colitis
Ulcerative colitis treatment in Hyderabad includes a combination of medications, lifestyle changes, and, in severe cases, surgical interventions. The treatment approach depends on the severity of the condition:
Medications:
- Aminosalicylates (5-ASAs): Reduce inflammation and prevent flare-ups.
- Corticosteroids: Used for moderate to severe symptoms to control inflammation.
- Immunosuppressants: Help suppress the immune response to prevent further damage.
- Biologics: Target specific proteins in the immune system to reduce inflammation.
Diet and Lifestyle Modifications:
Avoiding foods that cause triggers, such as dairy, spicy meals, and caffeine.
- Drinking plenty of water and eating a diet rich in fiber.
- Using meditation and yoga to manage stress.
Surgical Treatment:
- In severe cases, removal of the colon (colectomy) may be necessary.
- Restorative procedures like ileal pouch-anal anastomosis (IPAA) help maintain normal bowel function.
Why Choose Lux Hospitals for Ulcerative Colitis Treatment?
- Experienced Specialists: Hyderabad’s best Proctologists or gastroenterologists and colitis experts make up our team.
- Advanced Diagnostic Techniques: To make an accurate diagnosis, we employ state-of-the-art imaging and endoscopic techniques.
- Comprehensive Treatment Plans: Tailored therapies that suit each patient’s condition.
- State-of-the-Art Facilities: The newest technology for treating long-term gastrointestinal disorders is available at our hospital.
- Patient-Centred Approach: Our patients’ well-being is our priority, and we provide ongoing support and direction.
Testimonials
"laser treatment for my dad’s piles"
Dr. Samhitha Reddy’s laser treatment for my dad’s piles worked wonders. He’s pain-free now and really grateful for her care!

Mithilesh Sah
"smooth and painless"
Dr. Samhitha Reddy’s laser treatment for my fissure wassmooth and painless. She was super kind, which made the whole process much easier.

Rohit Kumar
"Colorectal Diseases"
Lux hospital is one of best hospital in Hyderabad for colorectal diseases. Dr. Samhita Mam is one the finest surgeon, very polite and explain everything in detail and the hospital staff is soo caring..Thank you so much..

Arti Shettiwar
"Admitted for my fistula surgery"
I was admitted for my fistula surgery, Dr Samhita has been very helpful in detecting the issue and explained the causes and prevention . Surgery was seamless and without pain.Also the support staff have been extremely helpful and were available every time. Keep up doing the great work.

Sanat Jayasingh
"Fistula Surgery"
We were admitted for fistula surgery and had to be under supervision for 24 hours. I could say that the staff including from the doctors and the Nurse and the house keeping staff, everyone was so polite and helpful and attending the patient within no time. Hospitalisation here was so smooth and Special thanks to Ashok(patient relationship manager) who is super polite and answering the questions related to insurance

Sujith V
Latest Health Articles by Lux
Frequently Asked Questions
The best treatment for ulcerative colitis depends on the severity of the condition. It may include medications (aminosalicylates, corticosteroids, immunosuppressants, biologics), lifestyle changes (diet modifications, stress management), and, in severe cases, surgery (colectomy).
Lux Hospitals has top colitis specialists who provide comprehensive care for patients with inflammatory bowel disease, including ulcerative colitis.
Lux Hospitals in Hyderabad is a leading healthcare facility for ulcerative colitis treatment. The hospital offers advanced diagnostic techniques, expert gastroenterologists, and personalized treatment plans.
The cost varies depending on the severity of the condition and the type of treatment required, such as medication, lifestyle management, or surgery. At Lux Hospitals, we offer tailored treatment plans with transparent pricing. Please contact us for a detailed estimate.
The exact cause of ulcerative colitis is unknown, but it is believed to result from an abnormal immune response, genetic factors, and environmental triggers.
Ulcerative colitis has no cure, but it can be managed with medications, lifestyle changes, and, in severe cases, surgery.
A low-fibre, well-balanced diet rich in lean proteins, healthy fats, and easily digestible foods like cooked vegetables, white rice, and bananas is best for ulcerative colitis. Avoid spicy, greasy, and high-fibre foods during flare-ups.
Yes, hormonal changes during the menstrual cycle can worsen ulcerative colitis symptoms, leading to increased bloating, cramping, and digestive discomfort.
Ulcerative colitis primarily affects the large intestine (colon) and rectum, causing inflammation and ulcers. It leads to symptoms like diarrhea, abdominal pain, and rectal bleeding.
You can book an appointment for Ulcerative Colitis treatment by calling, visiting the website, or walking into Lux Hospitals, Hyderabad. Consult Lux Hospitals for expert care.



















