Breast Lump Surgery in Hyderabad: Comprehensive Guide
Breast lumps are common in women and could be expected from hormonal changes, infections, or even tumors. Not all lumps are cancerous, but timely evaluation and proper breast lump treatment are important. If you have been noticing the symptoms of breast lumps, seeking expert advice from medical professionals can help to determine the best course of action to take.At Lux Hospitals, we provide the best breast lump treatment with top surgeons, ensuring accurate diagnosis and effective care.
What is Breast Lump Surgery?
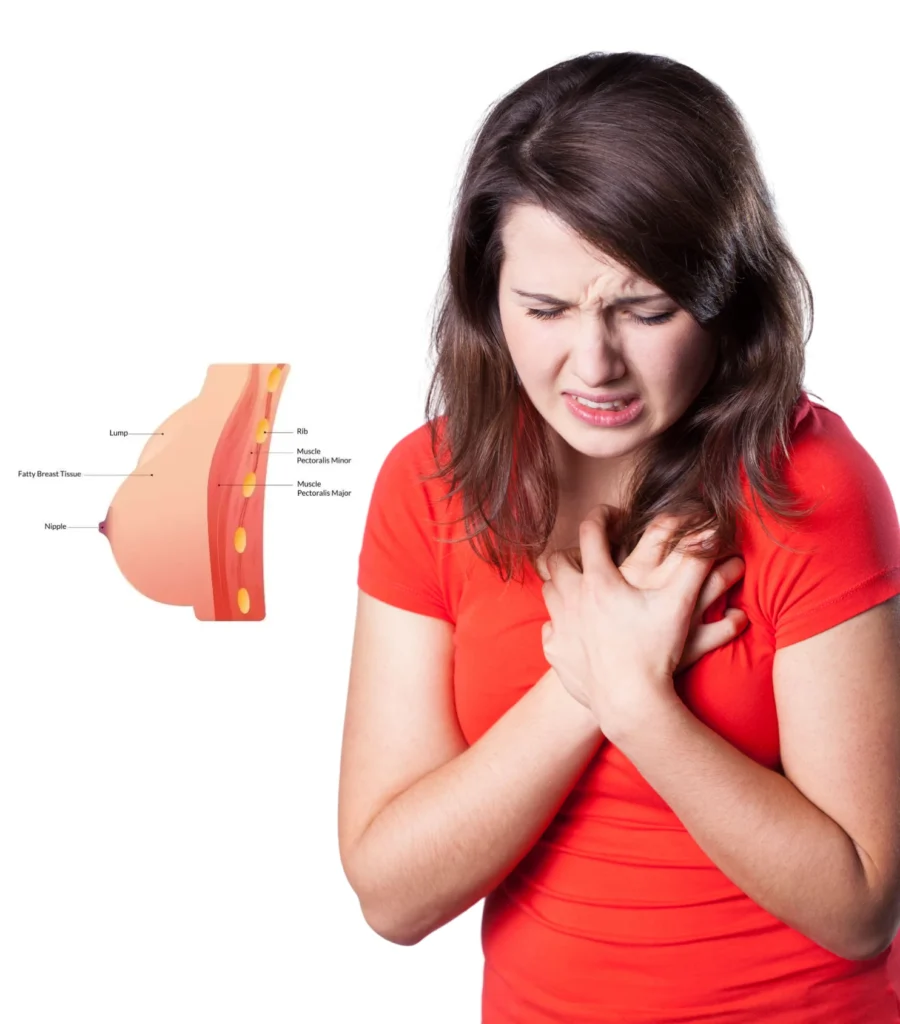
Breast lump surgery is a medical procedure performed to remove abnormal lumps from the breast tissue. It allows the diagnosis and management of benign and malignant lumps, thus keeping general breast health.
Types of Breast Lumps
- Benign Lumps: These are non-cancerous lumps, including fibroadenomas, cysts, or lipomas.
- Malignant Lumps: Cancerous lumps require immediate medical attention and often necessitate surgery.
- Hormonal Lumps: Often caused by hormonal fluctuations during menstruation, pregnancy, or menopause.
- Infectious Lumps: Formed due to bacterial infections leading to abscesses or mastitis.
Causes of Breast Lumps
Understanding the causes of breast lumps can aid in prevention and treatment. Some common causes include:
- Fibrocystic breast changes
- Hormonal fluctuations
- Breast infections or abscesses
- Injuries or trauma to the breast tissue
- Cancerous growths
Symptoms of Breast Lumps
Recognizing the symptoms early can help prompt breast lumps removal and prevent complications. Common symptoms include:
- A noticeable lump or thickening in the breast or underarm
- Changes in breast size or shape
- Skin dimpling or puckering
- Pain or tenderness in the lump area
- Discharge from the nipple
- Redness or swelling in the breast
Treatment Options for Breast Lumps
In case the lump is suspicious or turns painful, breast lump surgery at Lux Hospitals in Hyderabad is advised. The procedure involves removing the lump for further evaluation and treatment.
Types of Breast Lump Surgery
- Lumpectomy: Only the lump and a tiny amount of surrounding tissue are removed during this minimally invasive surgery.
- Mastectomy: Recommended for cancerous lumps involving partial or complete removal of breast tissue.
- Non-Invasive Breast Surgery: Advanced techniques like laser therapy or ultrasound-guided procedures that minimize tissue damage.
Breast Lump Surgery Process
- Pre-Surgical Consultation: Diagnosis through mammograms, ultrasounds, and biopsies.
- Surgical Procedure: Performed under general / local anesthesia.
- Recovery and Aftercare: Post-surgical monitoring, medications, and follow-up visits for healing and further treatment.
Who Needs Breast Lump Removal Surgery?
- Patients with persistent or growing lumps
- Those experiencing severe pain or discomfort
- Individuals with a history of breast cancer or genetic predisposition
- Cases where diagnostic tests indicate malignancy
Why Choose Breast Lump Treatment at Lux Hospitals in Hyderabad?
- Expert Breast Surgery Specialists : Receive care from top breast health experts at Lux Hospitals.
- Comprehensive Breast Health Services : From diagnosis to treatment, we offer complete breast care solutions.
- Minimally Invasive Procedures : Advanced non-invasive breast surgery options for faster recovery.
- Affordable & Advanced Lump Removal : Cutting-edge surgical techniques at cost-effective prices
Lux Hospitals offers personalised care, modern facilities, and reliable diagnosis and treatment for breast tumors.
Post-Surgery Care and Recovery
- Follow medication guidelines as prescribed.
- Avoid heavy lifting or strenuous activities for a few weeks.
- Regularly change dressings and maintain hygiene.
- Attend follow-up appointments for monitoring.
Testimonials
"She was well recovered with in 2 days"
My mother was suffering with Gallstone problem... Abhishek sir has given very good treatment... she was well recovered with in 2 days... Thank you sir... And staff and management also very soft in behaviour and nurse treatment also very good…

Reddy Narayana Reddy
"Worried about my hernia surgery"
I was worried about my hernia surgery, but Dr. Abhishek sir gave us confidence to undergo surgery. It took exactly 4 days for me to get back to normal after the surgery. Very happy with treatment

Raj Kamal
"My hubby is absolutely fine "
Hi Doctor, you have been extremely kind and patient towards the problem we went to visit you with. My hubby is absolutely fine after the surgery. And we whole heartedly thank you for that. Please be like this always.we wish you a magnificient career.

Sohini Banerjee
"Great experience from the review and till discharge"
Had surgery for removal of painful multiple lipomas ,had a great experience from the review and till discharge, finally satisfied in this place ,handled by Dr. Abhishek. Highly recommended, Lux hopsital for Lipomas Surgery in Hyderabad.

Ram Ram
"Helped me so much with my varicose veins. Surgery"
Lux Hospitals’ team really cares! They helped me so much with my varicose veins. Surgery done by Dr Abhishek sir. He is very experience surgeon. Doctor spoke with us very well and gave confidence to undergo surgery.

Bhushan Kumar
Latest Health Articles by Lux
Frequently Asked Questions
Recovery time for breast lump removal surgery varies but generally takes about 1 to 2 weeks. Most patients can resume normal activities within a few days, with complete healing in a few weeks.
The cost of breast lump removal surgery depends on factors such as the hospital, surgeon's expertise, procedure type, and additional tests or treatments required. For accurate pricing, it's best to consult Lux Hospitals directly.
Breast lump removal surgery is usually not painful as it is performed under anesthesia. Mild discomfort or soreness may occur after the procedure, which can be managed with pain relief medications.
Lux Hospitals offers expert breast surgeons, advanced technology, and minimally invasive options for faster recovery. With comprehensive care, transparent pricing, and a patient-focused approach, we ensure safe and effective breast lump removal.
Yes, Lux Hospitals offers minimally invasive breast lump removal procedures, ensuring faster recovery, less pain, and minimal scarring.
You can book an appointment online via the Lux Hospitals website, call our helpline, or visit the hospital directly.



















