Perianal Abscess vs Hemorrhoid Explained
It might be perplexing and concerning to have pain or discomfort in the anal region. This area is frequently affected by two conditions: hemorrhoids and perianal abscess. Despite their initial similarities, their causes, symptoms, and treatments are very different. Comprehending these distinctions is crucial for accurate diagnosis, and these differences are essential for proper diagnosis and prompt relief.
What is a Perianal Abscess?
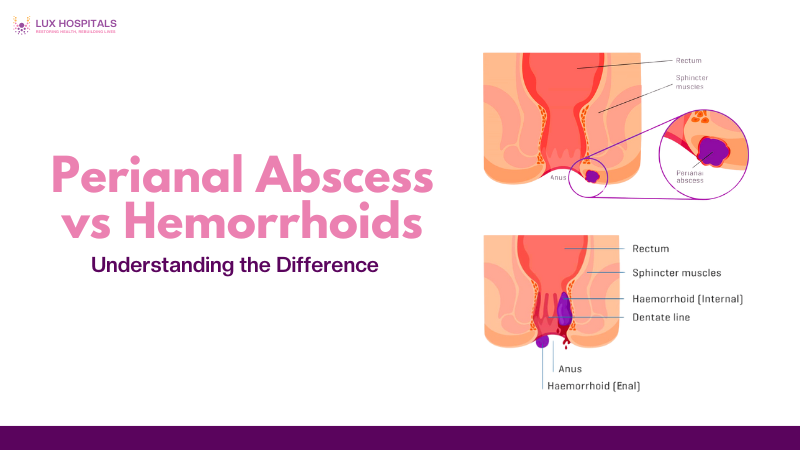
A perianal abscess is a painful collection of pus caused by a bacterial infection in the tissue around the anus or rectum. This condition develops rapidly and often requires urgent medical attention. Common symptoms include constant pain, swelling, redness, warmth, and sometimes fever. If left untreated, it can result in an anal fistula, a more dangerous condition.
Key Features of a Perianal Abscess:
- Caused by bacterial infection, usually from blocked anal glands.
- Sudden onset of pain, which worsens over time.
- may be accompanied by chills, fever, and exhaustion.
- Results in a red, swollen lump near the anus.
- If untreated, it can develop into a fistula (an abnormal channel between organs).
Common Risk Factors:
- Crohn’s disease or other inflammatory bowel disorders.
- Weakened immune system (HIV, diabetes).
- Recent anal injury or surgery.
- Poor hygiene or persistent infections.
Treatment typically involves incision, drainage, antibiotics, and proper wound care.
What are Hemorrhoids?
Similar to varicose veins, hemorrhoids are enlarged veins in the lower rectum or anus. They can appear outwardly (under the skin surrounding the anus) or internally (within the rectum). They may exist internally, that is, within the rectum. (inside the rectum) or external (under the skin around the anus) Symptoms include itching, rectal bleeding, and pain during bowel movements. Hemorrhoids are not caused by infection and rarely lead to serious complications.
Key features of hemorrhoids:
- Swollen veins in the rectum or anus
- Bright red bleeding during bowel movements
- Pain or discomfort while sitting or passing stool
- Itching or irritation around the anus
- Lump or swelling near the anal opening
Common risk factors include
- Low-fiber diet
- Straining during bowel movement
- Obesity or a sedentary lifestyle
- Prolonged sitting, especially on the toilet
Hemorrhoids are not infectious and can often be managed with lifestyle changes and over-the-counter treatments.
Comparison Table: Perianal Abscess vs Hemorrhoid
Feature | Perianal Abscess | Hemorrhoids |
Cause | Bacterial infection | Venous swelling |
Pain | Severe and constant | Mild to moderate, episodic |
Swelling | Red, tender lump | Soft, bluish lump |
Discharge | May release pus | Rarely any discharge |
Systemic Symptoms | Fever, chills | None |
Key Symptoms to Compare
Recognizing the different symptoms is crucial for determining whether the issue is a perianal abscess vs hemorrhoid.
Perianal Abscess:
- Sudden, intense pain
- Swelling that becomes firmer
- Fever and chills
- Warm, red skin around anus
- Pus discharge or foul-smelling drainage
Hemorrhoids:
- Bright red blood on the toilet paper
- Anal itching or burning
- Painless bleeding (internal haemorrhoids)
- Pain when sitting or passing stool (external haemorrhoids)
- Tissue bulging outside the anus
Diagnosis Process
A physical examination usually diagnoses both conditions, but some tests may help confirm the diagnosis.
Diagnosis includes:
- Digital rectal exam to feel for lumps or swelling
- Visual inspection for external issues
- Anoscopy or sigmoidoscopy for internal haemorrhoids
- Ultrasound or MRI for locating deep abscesses
Early diagnosis is vital in choosing the proper treatment for perianal abscess vs hemorrhoid and avoiding complications.
Treatment Options
Perianal Abscess Treatment:
- Surgical drainage is the most effective solution.
- Antibiotics are used to treat or prevent the spread of infection.
- Warm sitz baths to ease discomfort.
- Regular cleaning and wound dressing.
Hemorrhoid Treatment:
- A high-fiber diet to prevent straining.
- Topical creams or suppositories for relief.
- Warm baths and cold compresses.
- less intrusive techniques such as rubber band ligation or infrared coagulation.
- Hemorrhoidectomy in severe, persistent cases.
Understanding these options helps patients manage their condition, whether perianal abscess vs hemorrhoid.
Potential Complications
From Perianal Abscess:
- Chronic fistulas
- Sepsis or bloodstream infections
- Recurrence if not fully drained
From Hemorrhoids:
- Thrombosis (blood clot inside the haemorrhoid)
- Prolapse, causing hygiene problems
- Chronic bleeding, leading to anaemia
Each condition has unique risks that can escalate without proper care.
Prevention Tips
Preventing Hemorrhoids:
- Eat fibre-rich foods (vegetables, fruits, whole grains)
- Avoid sitting too long, especially on the toilet
- Stay hydrated
- Regular physical activity
- Avoid straining when passing stool
Preventing Perianal Abscess:
- Maintain anal hygiene
- Treat minor infections early
- Manage underlying conditions like Crohn’s disease
- Avoid anal trauma or unnecessary pressure
Prevention plays a significant role in reducing the occurrence of perianal abscesses vs. hemorrhoids.
Conclusion
Effective management of anal pain requires an understanding of the distinction between hemorrhoids vs perianal abscesses. Both may result in pain and edema, but they have different causes, dangers, and therapies. Seek medical advice immediately if you notice unusual symptoms—especially fever, discharge, or worsening pain. With proper care and prevention, both conditions are treatable. A perianal abscess is a painful, pus-filled infection, often requiring drainage and possibly antibiotics, while hemorrhoids are swollen veins that may cause itching, bleeding, and discomfort, typically managed with lifestyle changes and topical treatments. It’s crucial to differentiate between the two, as perianal abscesses may require more urgent medical attention.
Frequently Asked Questions
A perianal abscess usually presents as a swollen, red, and painful lump with fever or chills. Hemorrhoids, in contrast, tend to cause itching, discomfort, and sometimes bleeding without systemic symptoms. If the area feels hot to the touch and the pain is deep or throbbing, it’s likely an abscess
Yes, hemorrhoids are far more common and affect a larger portion of the population. Lifestyle factors generally cause them and can often be managed without medical intervention. Perianal abscesses are less common and usually indicate infection, requiring surgical attention.
While rare, a thrombosed or irritated hemorrhoid may become secondarily infected, leading to abscess formation. More often, perianal abscesses develop independently from anal glands. Poor hygiene, scratching, or hemorrhoidal tissue trauma could introduce infection
A perianal abscess is typically more painful, with sharp or throbbing sensations, and often accompanied by fever. Hemorrhoids can be very uncomfortable but usually cause mild to moderate pain, especially during bowel movements. Systemic symptoms are often indicative of an abscess. The degree and intensity of pain can be used to distinguish between hemorrhoids and perianal abscesses.
Yes, a perianal abscess can be mistaken for hemorrhoids because both conditions may cause anal pain and swelling. However, abscesses tend to cause more severe pain, fever, and a feeling of fullness or pressure. Prompt diagnosis by a healthcare provider is important to avoid complications.