When to See a Doctor for Uterine Polyps: Key Symptoms Women Shouldn’t Ignore
Because they believe irregular menstruation symptoms are transient, many women ignore them. However, uterine polyps, a frequent gynecological issue, may be indicated by changes in bleeding patterns. These uterine growths are often not malignant, but if left untreated, they can interfere with everyday living and fertility. Maintaining reproductive health requires prompt medical attention and early awareness. At Lux Hospital, women receive expert evaluation and personalized treatment for Uterine Polyps, ensuring long-term well-being and peace of mind.
Noticing Irregular Periods or Spotting? Don’t Ignore the Signs.
👉 Schedule a Gynecology Checkup at Lux Hospitals
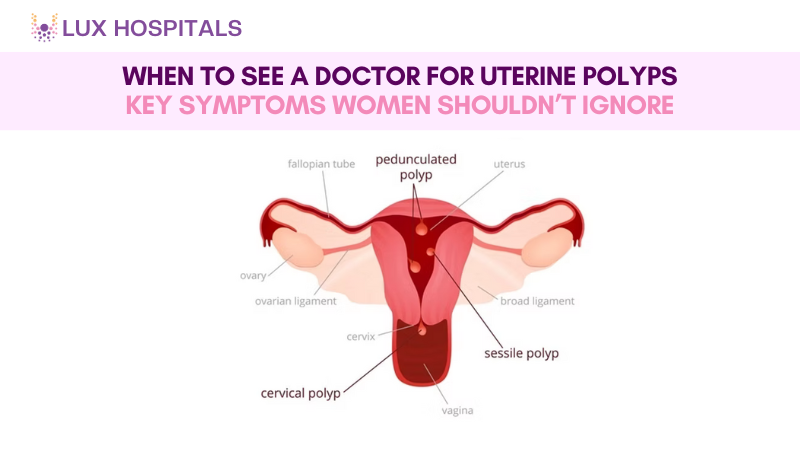
What Are Uterine Polyps?
Uterine Polyps are abnormal tissue growths that form from the uterine lining, also known as the endometrium. They can range from a few millimeters to several centimeters in size and may appear alone or in groups.
Key Features of Uterine Polyps
- Usually benign and slow-growing
- Common in women aged 40–50
- Linked to hormonal imbalance, especially estrogen
- May cause symptoms or remain silent
Want to Know If Your Symptoms Match Uterine Polyps?
👉 Consult Our Women’s Health Specialist at Lux Hospitals
Typical Symptoms Women Shouldn’t Ignore
Uterine polyps can cause mild to severe symptoms. Early detection of these symptoms can help avoid problems.
Abnormal Menstrual Bleeding
- Heavy or prolonged periods
- Bleeding between cycles
- Irregular menstrual patterns
Following Menopause
A warning indicator of uterine polyps or other disorders that need to be evaluated right away is postmenopausal bleeding.
Pelvic Pain or Pressure
Large polyps may cause discomfort, cramping, or a feeling of pressure in the lower abdomen.
Fertility Problems
Uterine Polyps may block implantation or increase miscarriage risk, making conception difficult.
Postmenopausal Bleeding or Planning Pregnancy? Don’t Delay
👉 Consult Gynecology & Fertility Experts at Lux Hospitals
Causes and Risk Factors
The exact cause of Uterine Polyps is not fully understood, but hormonal changes play a major role.
Common Risk Factors
- High estrogen levels
- Obesity
- High blood pressure
- Hormone therapy or tamoxifen use
- Family history of gynecological conditions
Concerned About Your Hormonal Health?
👉 Get a Preventive Women’s Health Screening
When Should You See a Doctor for Uterine Polyps?
You should consult a gynecologist if symptoms persist or worsen over time. Medical attention is necessary when:
- Menstrual bleeding becomes unusually heavy
- Bleeding occurs after menopause
- Periods become unpredictable
- Fertility issues remain unexplained
Lux Hospital specialists use advanced diagnostic methods to identify Uterine Polyps early and recommend appropriate treatment.
Looking for Safe, Advanced Treatment for Uterine Polyps?
👉 Book Your Consultation with Lux Hospitals
How Are Uterine Polyps Diagnosed?
A precise diagnosis is necessary for efficient treatment.
Diagnostic Tests
- Endometrial biopsy to rule out malignant changes
- Hysteroscopy to see the uterus directly
- Transvaginal ultrasound to identify abnormal growths
Treatment Options for Uterine Polyps
The size of the polyp, future pregnancy plans, and symptoms all influence the course of treatment.
Non-Surgical Management
- Observation for small, symptom-free polyps
- Hormonal medications to reduce symptoms
Surgical Treatment
- Hysteroscopic polypectomy is a minimally invasive procedure. This is commonly performed at Lux Hospital with quick recovery and excellent outcomes.
Possible Complications If Left Untreated
Untreated Uterine Polyps can lead to:
- Chronic heavy bleeding and anemia
- Increased infertility risk
- Rare progression to cancer
Timely care significantly reduces these risks.
Take Charge of Your Reproductive Health Today.
👉 Call or Book an Appointment Online at Lux Hospitals
Conclusion
Women can seek prompt medical attention and prevent complications by being aware of the symptoms of uterine polyps. Reproductive results and quality of life are enhanced by early diagnosis and proper treatment. Lux Hospital, which provides skilled gynecological treatments, cutting-edge technology, and compassionate care, is still a reliable choice for women’s healthcare. The experts at Lux Hospital are available to assist you on your path to improved health if you suspect uterine polyps.
Frequently Asked Questions
Hormonal imbalances, particularly high amounts of estrogen, are the primary cause of uterine polyps. They are more prevalent during menopause or perimenopause. Certain drugs and obesity can raise the risk.
Most uterine polyps are benign and non-cancerous. A small percentage may show precancerous or cancerous changes. Risk is higher in postmenopausal women.
Small uterine polyps may shrink naturally over time. However, symptomatic polyps usually persist. Medical evaluation helps determine proper management.
Uterine polyps can obstruct the implantation of an embryo. They may result in repeated miscarriages or infertility. Pregnancy outcomes are frequently improved by removal.
Removal is done using minimally invasive hysteroscopy. The procedure is performed under anesthesia. Most women recover quickly with minimal discomfort.